103 Trigonometry Problems
103 Trigonometry Problems
103 Trigonometry Problems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1. Trigonometric Fundamentals 43<br />
y<br />
✻<br />
y<br />
✻<br />
B<br />
<br />
A<br />
✏ ❆❆❑ ✟<br />
✟ ✟✟✟✟✟✟✟✟✯<br />
✲<br />
O<br />
x<br />
✏✏✏✏✏✏✏✏<br />
✏✶<br />
A ′<br />
<br />
C′<br />
✏✶<br />
A<br />
<br />
❃✚ ✏ ✲<br />
✚✚✚✚✚❃ ✏✏✏✏✏✏✏✏✏✏ ✲✚ ✚✚✚✚✚❃✲ ✲<br />
O B<br />
B ′ x<br />
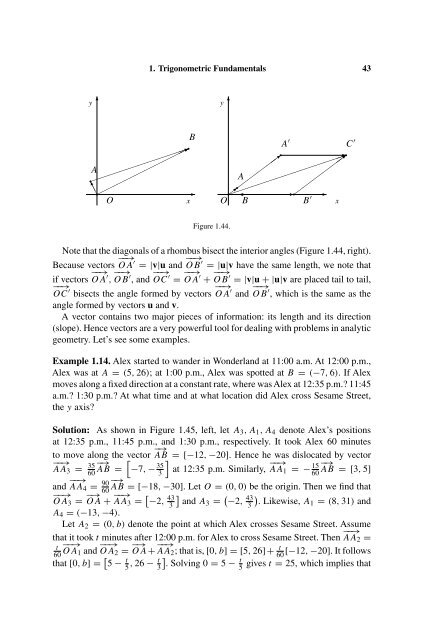
Figure 1.44.<br />
Note that the diagonals of a rhombus bisect the interior angles (Figure 1.44, right).<br />
Because vectors −−→ OA ′ =|v|u and OB −−→ ′ =|u|v have the same length, we note that<br />
if vectors −−→ OA ′ , OB −−→ ′ , and OC −−→ ′ = −−→ OA ′ + OB −−→ ′ =|v|u +|u|v are placed tail to tail,<br />
−−→<br />
OC ′ bisects the angle formed by vectors −−→ OA ′ and OB −−→ ′ , which is the same as the<br />
angle formed by vectors u and v.<br />
A vector contains two major pieces of information: its length and its direction<br />
(slope). Hence vectors are a very powerful tool for dealing with problems in analytic<br />
geometry. Let’s see some examples.<br />
Example 1.14. Alex started to wander in Wonderland at 11:00 a.m. At 12:00 p.m.,<br />
Alex was at A = (5, 26); at 1:00 p.m., Alex was spotted at B = (−7, 6). If Alex<br />
moves along a fixed direction at a constant rate, where was Alex at 12:35 p.m.? 11:45<br />
a.m.? 1:30 p.m.? At what time and at what location did Alex cross Sesame Street,<br />
the y axis?<br />
Solution: As shown in Figure 1.45, left, let A 3 ,A 1 ,A 4 denote Alex’s positions<br />
at 12:35 p.m., 11:45 p.m., and 1:30 p.m., respectively. It took Alex 60 minutes<br />
to move along the vector −→ AB =[−12, −20]. Hence he was dislocated by vector<br />
−−→<br />
AA 3 =<br />
60<br />
35 −→<br />
[ ]<br />
AB = −7, − 35 3<br />
at 12:35 p.m. Similarly, AA −−→<br />
1 =−60<br />
15 −→<br />
AB =[3, 5]<br />
and −−→ AA 4 = 90 −→<br />
60AB =[−18, −30]. Let O = (0, 0) be the origin. Then we find that<br />
−−→<br />
OA 3 = −→ OA + AA −−→<br />
3 = [ −2, 43 ]<br />
3 and A3 = ( −2, 43 )<br />
3 . Likewise, A1 = (8, 31) and<br />
A 4 = (−13, −4).<br />
Let A 2 = (0,b) denote the point at which Alex crosses Sesame Street. Assume<br />
that it took t minutes after 12:00 p.m. for Alex to cross Sesame Street. Then −−→ AA 2 =<br />
t −−→<br />
60OA 1 and OA −−→<br />
2 = −→ OA+ −−→ AA 2 ; that is, [0,b]=[5, 26]+<br />
60 t [−12, −20]. It follows<br />
that [0,b]= [ 5 −<br />
5 t , 26 − 3] t . Solving 0 = 5 −<br />
t<br />
5<br />
gives t = 25, which implies that