Assessment, Conservation and Sustainable Use of Forest Biodiversity
Assessment, Conservation and Sustainable Use of Forest Biodiversity
Assessment, Conservation and Sustainable Use of Forest Biodiversity
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Assessment</strong>, <strong>Conservation</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sustainable</strong> <strong>Use</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Forest</strong> <strong>Biodiversity</strong><br />
11<br />
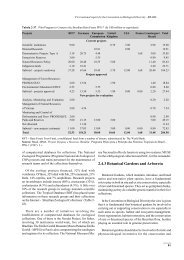
GENETIC SPECIALTIES OF CONIFEROUS TREE GEOGRAPHICAL<br />
POPULATIONS ON THE NORTH-WEST OF RUSSIA<br />
Marina Nikolaeva, Natalia Pelevina<br />
Institutsky Pr., 21, Saint-Petersburg<br />
<strong>Forest</strong>ry Research<br />
Institute<br />
Keywords: geographic crops, genotype, growth, preservation, origin <strong>of</strong> seeds, inheritance, seed breed<br />
Background<br />
The study <strong>of</strong> variability, proceed from the formula: genotype = phenotype + environment, has purpose to<br />
reveal the distribution <strong>of</strong> intraspecific diversity in populations, that is the study <strong>of</strong> geographical variation <strong>of</strong><br />
species (<strong>and</strong> kind) in connection with environment (Pravdin, 1973). One <strong>of</strong> the main methods for this study<br />
is creation <strong>of</strong> net <strong>of</strong> the geographical crops. Proceed from the All-Union program <strong>of</strong> 1972 year on the northwest<br />
<strong>of</strong> the country geographical crops <strong>of</strong> Coniferous tree are planted in 4 regions: Leningrad, Vologda, Pskov,<br />
Iaroslavl. In the most complete way specific diversity is presented in cultivations <strong>of</strong> Leningrad region: pine,<br />
spruce, <strong>and</strong> introductional breed – larch <strong>and</strong> cedar pine.<br />
Study System<br />
In the capacity <strong>of</strong> the united document for Russia was accepted the method (1972). Now these young st<strong>and</strong>s<br />
are from 17 to 25 years. The number <strong>of</strong> acounted trees is not less than 150 per variant. At the different age<br />
stages preservation <strong>and</strong> conditions <strong>of</strong> plantations, mean growth parameters – diameter <strong>and</strong> height were<br />
determined. Mean height was determined by height graphs. More detailed research works were conducted in<br />
the spruce crops on recognition <strong>of</strong> forms – properties in the frame <strong>of</strong> population.<br />
Results <strong>and</strong> discussions<br />
Different reaction <strong>of</strong> aboriginal provenances – pine <strong>and</strong> spruce, to the change <strong>of</strong> climatic conditions is<br />
observed. North forms <strong>of</strong> Scotch pine, including its subspecies P. lapponica, genetically are more stable against<br />
mushroom disease shutte, which has took place at the earliest stages <strong>of</strong> plants development. And when crops<br />
are 22 years old climatypes with, provenance from coniferous forest zone (59° – 63° North) had 50-66%<br />
preservation, to 8% from steppe zone; connection <strong>of</strong> preservation with latitude remain invariable<br />
considerable, r =0,67. During the period <strong>of</strong> observation in geographical cultivation <strong>of</strong> spruce is retraced<br />
lowering <strong>of</strong> stability to new growing conditions <strong>of</strong> north breeds, r = -0,50, <strong>and</strong> east , r = -0,27. Climatypes <strong>of</strong><br />
Picea abies <strong>and</strong> P. fennica with properties P. abies are marked good preservation, 58-80% , (54,4° –61,7° North;<br />
25,6° –37,0° East). Till 5-10 years the growth <strong>of</strong> crops to greater degree was defined by technological factor <strong>and</strong><br />
soil conditions, than by genetic <strong>and</strong> physiology-ecological peculiarities <strong>of</strong> seed breed. The age <strong>of</strong> 9-10-years is<br />
a period <strong>of</strong> the beginning <strong>of</strong> closing the crowns in rows, when competitive relations among trees arise, it is<br />
characterized by diminution <strong>of</strong> increase in high on 5-10% (Kairjukshtis, 1976). The share <strong>of</strong> genotypical<br />
influence on speed <strong>of</strong> growth is reducing, rang status <strong>of</strong> coniferous climatypes, become smooth. At the<br />
following closing <strong>of</strong> crowns mutual oppression weaken <strong>and</strong> the current increase rise again. The more to the<br />
north <strong>and</strong> east the point <strong>of</strong> pine seeds storage is, the worse growth is to the end <strong>of</strong> the first age class, as in<br />
height (r = -0,41; r = -0,31), so in diameter (r =-0,55;r = -0,44). The best variants are – from zone <strong>of</strong> deciduous<br />
forests; the more heigh are (middle H = 10,0 m) – Pskov, Mogilev, Moscow. Among climatypes from zone <strong>of</strong><br />
coniferous forests local – Laningrad sharply differs at speed <strong>of</strong> growth. In the majority <strong>of</strong> breeds <strong>of</strong> Picea abies<br />
is observed tendency <strong>of</strong> rise in rang (Pskov is the leader, middle H=8,2 m). Climatypes <strong>of</strong> P.sibirica <strong>and</strong><br />
P.fennica (Murmansk, Archangelsk, Perm, Sverdlovsk, Tatar, Kirov region <strong>and</strong> central part <strong>of</strong> Karelia),<br />
continue falling behind in growth.<br />
46