Fibrate Mechanism of Action - The Center for Cholesterol Management
Fibrate Mechanism of Action - The Center for Cholesterol Management
Fibrate Mechanism of Action - The Center for Cholesterol Management
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
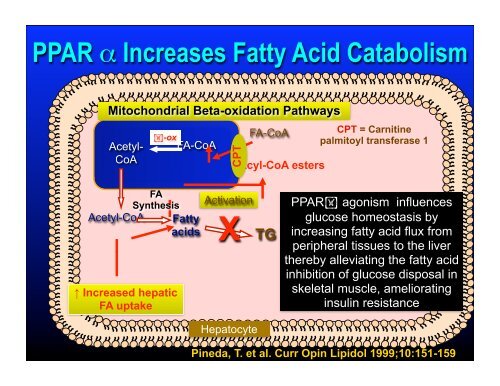
PPAR α Increases Fatty Acid Catabolism<br />
Mitochondrial Beta-oxidation Pathways<br />
Acetyl-<br />
CoA<br />
apple-ox<br />
FA-CoA<br />
CPT<br />
FA-CoA<br />
Acyl-CoA esters<br />
CPT = Carnitine<br />
palmitoyl transferase 1<br />
FA<br />
Synthesis<br />
Acetyl-CoA Fatty<br />
acids<br />
↑ Increased hepatic<br />
FA uptake<br />
Activation<br />
X<br />
TG<br />
PPARapple agonism influences<br />
glucose homeostasis by<br />
increasing fatty acid flux from<br />
peripheral tissues to the liver<br />
thereby alleviating the fatty acid<br />
inhibition <strong>of</strong> glucose disposal in<br />
skeletal muscle, ameliorating<br />
insulin resistance<br />
Hepatocyte<br />
Pineda, T. et al. Curr Opin Lipidol 1999;10:151-159