Fibrate Mechanism of Action - The Center for Cholesterol Management
Fibrate Mechanism of Action - The Center for Cholesterol Management
Fibrate Mechanism of Action - The Center for Cholesterol Management
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
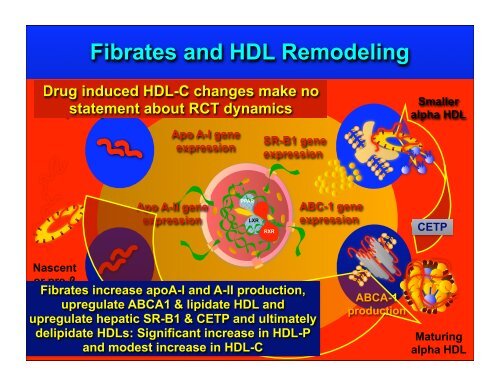
<strong>Fibrate</strong>s and HDL Remodeling<br />
Drug induced HDL-C changes make no<br />
statement about RCT dynamics<br />
Apo A-I production<br />
Apo A-I gene<br />
expression<br />
SR-B1 gene<br />
expression<br />
Smaller<br />
alpha HDL<br />
Apo A-II gene<br />
expression<br />
PPAR<br />
LXR<br />
RXR<br />
ABC-1 gene<br />
expression<br />
CETP<br />
Nascent<br />
or pre-β<br />
<strong>Fibrate</strong>s HDL Apo increase A-II apoA-I and A-II production,<br />
upregulate production ABCA1 & lipidate HDL and<br />
upregulate hepatic SR-B1 & CETP and ultimately<br />
delipidate HDLs: Significant increase in HDL-P<br />
and modest increase in HDL-C<br />
ABCA-1<br />
production<br />
Maturing<br />
alpha HDL