Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3 · <strong>Decision</strong> <strong>Support</strong> <strong>Model</strong> (<strong>IUWS</strong>-<strong>DSM</strong>) 87<br />
Very importantly, the user friendly Graphical User Interface (GUI) must be developed, so<br />
that the software can be easily controlled by water engineers and city planners. Moreover,<br />
the function of guidance, prompts, and instant help should be embedded, too. For example,<br />
the compulsory and optional items of input can be labelled with different backgrounds and<br />
likewise, the user input values and default values can be displayed in different colours.<br />
As two main modules, <strong>Model</strong> Engine and Database are explained a bit more as follows.<br />
3.6.2 <strong>Model</strong> engine<br />
Most functions and tasks are achieved by the model engine. Based on the planning<br />
procedure established in § 3.2, the calculation and comparison that are introduce in § 3.4<br />
and § 3.5 are realised by the model engine. Though the decision making polices developed<br />
in § 3.3 are stored in the database, the model engine has the right to control and call them to<br />
infer the solutions. The model engine is in charge of the communication between model<br />
users and the <strong>IUWS</strong>-<strong>DSM</strong>, other software and the <strong>IUWS</strong>-<strong>DSM</strong>, as well as between modules<br />
inside the <strong>IUWS</strong>-<strong>DSM</strong>.<br />
3.6.3 Database<br />
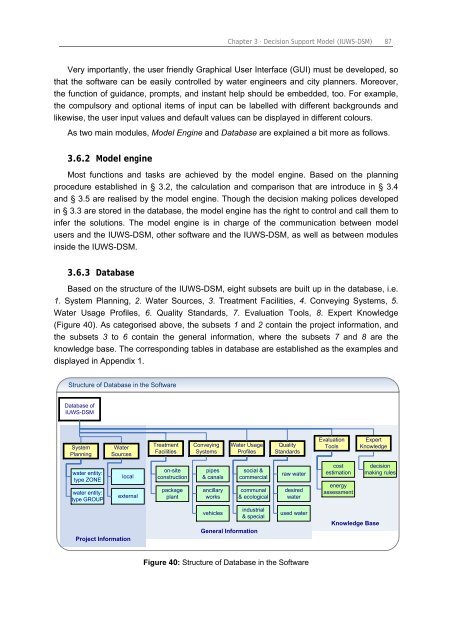
Based on the structure of the <strong>IUWS</strong>-<strong>DSM</strong>, eight subsets are built up in the database, i.e.<br />
1. System Planning, 2. Water Sources, 3. Treatment Facilities, 4. Conveying Systems, 5.<br />
Water Usage Profiles, 6. Quality Standards, 7. Evaluation Tools, 8. Expert Knowledge<br />
(Figure 40). As categorised above, the subsets 1 and 2 contain the project information, and<br />
the subsets 3 to 6 contain the general information, where the subsets 7 and 8 are the<br />
knowledge base. The corresponding tables in database are established as the examples and<br />
displayed in Appendix 1.<br />
Structure of Database in the Software<br />
Database of<br />
<strong>IUWS</strong>-<strong>DSM</strong><br />
System<br />
Planning<br />
water entity:<br />
type ZONE<br />
water entity:<br />
type GROUP<br />
Water<br />
Sources<br />
local<br />
external<br />
Project Information<br />
Treatment<br />
Facilities<br />
on-site<br />
construction<br />
package<br />
plant<br />
Conveying<br />
Systems<br />
pipes<br />
& canals<br />
ancillary<br />
works<br />
vehicles<br />
Water Usage<br />
Profiles<br />
social &<br />
commercial<br />
communal<br />
& ecological<br />
industrial<br />
& special<br />
General Information<br />
Quality<br />
Standards<br />
raw water<br />
desired<br />
water<br />
used water<br />
Figure 40: Structure of Database in the Software<br />
Evaluation<br />
Tools<br />
cost<br />
estimation<br />
energy<br />
assessment<br />
Expert<br />
Knowledge<br />
Knowledge Base<br />
decision<br />
making rules