Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2 · New Conception 25<br />
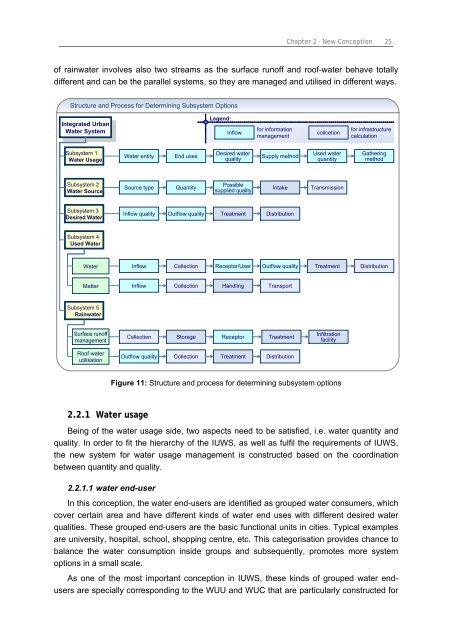
of rainwater involves also two streams as the surface runoff and roof-water behave totally<br />
different and can be the parallel systems, so they are managed and utilised in different ways.<br />
Structure and Process for Determining Subsystem Options<br />
Integrated Urban<br />
Water System<br />
Subsystem 1<br />
Water Usage<br />
Subsystem 2<br />
Water Source<br />
Subsystem 3<br />
Desired Water<br />
Subsystem 4<br />
Used Water<br />
Inflow quality Outflow quality Treatment Distribution<br />
Water Inflow Collection Receptor/User Outflow quality<br />
Matter Inflow Collection Handling Transport<br />
Subsystem 5<br />
Rainwater<br />
Surface runoff<br />
management<br />
Roof-water<br />
utilisation<br />
Collection<br />
2.2.1 Water usage<br />
Water entity End uses<br />
Source type Quantity<br />
Legend:<br />
Desired water<br />
quality<br />
Storage Receptor<br />
Outflow quality Collection Treatment<br />
for information<br />
Inflow collcetion<br />
management<br />
Possible<br />
supplied quality<br />
Supply method<br />
Treatment<br />
Distribution<br />
Used water<br />
quantity<br />
Intake Transmission<br />
Treatment<br />
Infiltration<br />
facility<br />
Figure 11: Structure and process for determining subsystem options<br />
for infrastructure<br />
calculation<br />
Gathering<br />
method<br />
Distribution<br />
Being of the water usage side, two aspects need to be satisfied, i.e. water quantity and<br />
quality. In order to fit the hierarchy of the <strong>IUWS</strong>, as well as fulfil the requirements of <strong>IUWS</strong>,<br />
the new system for water usage management is constructed based on the coordination<br />
between quantity and quality.<br />
2.2.1.1 water end-user<br />
In this conception, the water end-users are identified as grouped water consumers, which<br />
cover certain area and have different kinds of water end uses with different desired water<br />
qualities. These grouped end-users are the basic functional units in cities. Typical examples<br />
are university, hospital, school, shopping centre, etc. This categorisation provides chance to<br />
balance the water consumption inside groups and subsequently, promotes more system<br />
options in a small scale.<br />
As one of the most important conception in <strong>IUWS</strong>, these kinds of grouped water endusers<br />
are specially corresponding to the WUU and WUC that are particularly constructed for