Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Chapter 3 Decision Support Model (IUWS-DSM) - Tubdok
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
56 New Conception and <strong>Decision</strong> <strong>Support</strong> <strong>Model</strong> for <strong>IUWS</strong><br />
water usage<br />
& sources<br />
decision making positions<br />
subsystem<br />
applicability options<br />
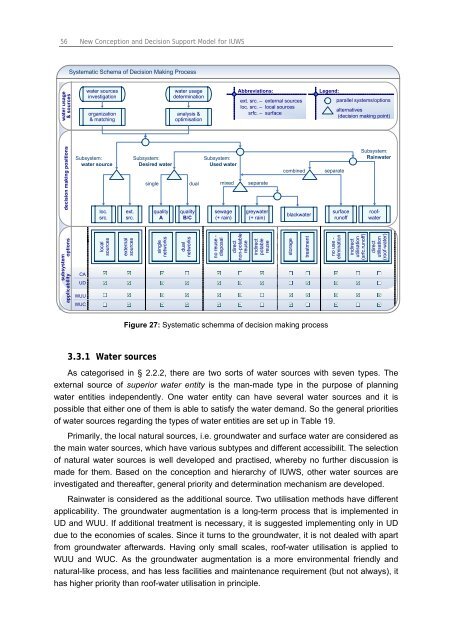
Systematic Schema of <strong>Decision</strong> Making Process<br />
water sources<br />
investigation<br />
organization<br />
& matching<br />
Subsystem:<br />
water source<br />
CA<br />
UD<br />
WUU<br />
WUC<br />
loc.<br />
src.<br />
local<br />
sources<br />
ext.<br />
src.<br />
external<br />
sources<br />
Subsystem:<br />
Desired water<br />
3.3.1 Water sources<br />
quality<br />
A<br />
water usage<br />
determination<br />
analysis &<br />
optimisation<br />
single dual<br />
single<br />
networks<br />
quality<br />
B/C<br />
dual<br />
networks<br />
Subsystem:<br />
Used water<br />
mixed separate<br />
sewage<br />
(+ rain)<br />
no reuse -<br />
disposal<br />
Abbreviations:<br />
ext. src. – external sources<br />
loc. src. – local sources<br />
srfc. – surface<br />
direct<br />
non-potable<br />
reuse<br />
greywater<br />
(+ rain)<br />
indirect<br />
potable<br />
reuse<br />
combined separate<br />
blackwater<br />
Figure 27: Systematic schemma of decision making process<br />
storage<br />
treatment<br />
Legend:<br />
parallel systems/options<br />
surface<br />
runoff<br />
no use -<br />
elimination<br />
alternatives<br />
(decision making point)<br />
indirect<br />
utilisation<br />
(srfc.runoff)<br />
Subsystem:<br />
Rainwater<br />
As categorised in § 2.2.2, there are two sorts of water sources with seven types. The<br />
external source of superior water entity is the man-made type in the purpose of planning<br />
water entities independently. One water entity can have several water sources and it is<br />
possible that either one of them is able to satisfy the water demand. So the general priorities<br />
of water sources regarding the types of water entities are set up in Table 19.<br />
Primarily, the local natural sources, i.e. groundwater and surface water are considered as<br />
the main water sources, which have various subtypes and different accessibilit. The selection<br />
of natural water sources is well developed and practised, whereby no further discussion is<br />
made for them. Based on the conception and hierarchy of <strong>IUWS</strong>, other water sources are<br />
investigated and thereafter, general priority and determination mechanism are developed.<br />
Rainwater is considered as the additional source. Two utilisation methods have different<br />
applicability. The groundwater augmentation is a long-term process that is implemented in<br />
UD and WUU. If additional treatment is necessary, it is suggested implementing only in UD<br />
due to the economies of scales. Since it turns to the groundwater, it is not dealed with apart<br />
from groundwater afterwards. Having only small scales, roof-water utilisation is applied to<br />
WUU and WUC. As the groundwater augmentation is a more environmental friendly and<br />
natural-like process, and has less facilities and maintenance requirement (but not always), it<br />
has higher priority than roof-water utilisation in principle.<br />
roofwater<br />
direct<br />
utilisation<br />
(roof-water)