Volume 61 Issue 2 (2011) - Годишник на ТУ - София - Технически ...
Volume 61 Issue 2 (2011) - Годишник на ТУ - София - Технически ...
Volume 61 Issue 2 (2011) - Годишник на ТУ - София - Технически ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
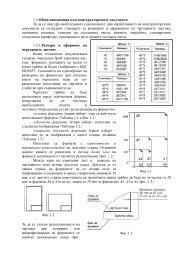
the rotor and the stator fields and it is greatly affected by the configuration of the rotorpermanent magnets and stator teeths. Pole shape improvement can be performed usingmodern optimization methods to obtain better magnetic field distribution. [1]From the mathematical point of view, optimization is a process of finding global maximum(or minimum) of some objective function. There are several approaches to thisproblem. One class of optimization techniques uses well-known conjugate-gradient(CG) methods for solving systems of linear equations, and Quasi-Newton (QN) methodsfor the non-linear case. Another class is so-called Simplex method, using the conceptof a simplex in choosing in which direction to lead the search. Both these techniquesare considered local in that the solution they find is highly dependent on the initialpoint of search. They can never guarantee that the solution is really the best, butdue to their usual tight connection with the problem, they tend to converge to the solutionrelatively quickly. Another problem with local techniques is that all of themimpose some constraints on the objective function in terms of continuity and differentiability,which are sometimes impossible to achieve. Very different class from theseis stochastic optimization. Techniques that fall into this category are consideredglobal and they usually work with population of candidate solutions, not just with onesolution, using probabilistic transitions between points in search space. Since theyusually do not use any knowledge about the problem, their convergence is slower thanthat of local techniques. But the fact that they can work with any kind of optimizationfunction, being it noncontinuous, non-differentiable, or with any kind of constraints,gives global techniques a great potential for use in various fields where finding thebest solution is more important than the convergence time. Different stochastic methodsare developed: genetic algorithms (GA), evolution strategies, Monte Carlo, simulatedannealing, particle swarm, etc. GA is one of the methods that proved to be goodin solving problems in electromagnetics – they are robust enough and easily implementedin the same time. [1-5, 10]2. Optimization process realizationOptimization is made by genetic algorithm toolbox of Matlab which employs theFemm model true Octave/Lua interface.Finite element method is used to solve electromagnetic problem. The Femm softwarepackage [7] was employed. Computations were automated using Octave-Femm library.Fig.1.Octave/Lua interface is a Matlab toolbox that allows for the operation of Finite ElementMethod Magnetics (Femm) via a set of Matlab functions. The toolbox workswith Octave, a Matlab clone. When Octave-Femm starts up a Femm process, the usualFemm user interface is displayed and is fully functional. The user then has thechoice of accomplishing modeling and analysis tasks either exclusively through functionsimplemented by the toolbox, or by a combination of manual and programmaticoperations – whichever is easiest for the task at hand. The syntax of the Octave-Femmtoolbox closely mirrors that of Femm’s existing Lua scripting language interface associatedwith Femm v4.2. However, there are some differences between the Lua functionsand the analogous Octave/Matlab implementations. [8, 9]106