- Page 1 and 2:
ISSN 1311-0829ГОДИШНИК НА
- Page 3 and 4:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 5 and 6:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 7:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 10 and 11:
• If a neutral element 1 of the s
- Page 12 and 13:
Proof. (i) Since for arbitrary ≀
- Page 14 and 15:
)is the endomorphism ≀ 0, . . . ,
- Page 16 and 17:
∣∣E (k)C n∣ ∣∣ =Propositi
- Page 18 and 19:
For k = 0 and s = 1 from the last p
- Page 20 and 21:
Facts concerning semilattices can b
- Page 22 and 23:
described by the following join-tab
- Page 24 and 25:
Finally we observe{aj , if i = k(f
- Page 26 and 27:
Let us consider the endomorphisms f
- Page 28 and 29:
Proposition 3.8 For any n ≥ 2 in
- Page 30 and 31:
Cryptographic protocols based on DL
- Page 32 and 33:
2.5 Bi-Semigroup Action Problem (BS
- Page 35 and 36:
Theorem 4.5 [14]. In the center of
- Page 37 and 38:
The only way we know for an attacke
- Page 39 and 40:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 41 and 42:
The exact definitions of points and
- Page 43 and 44:
FirstIterationSecondIterationx 0 0
- Page 45 and 46:
* x4. Order of approximationBecause
- Page 47 and 48:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 49 and 50:
генератори, присъе
- Page 55 and 56:
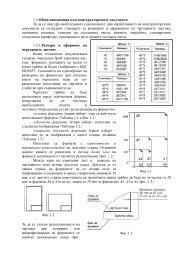
№ РежимТабл.4.1 Бала
- Page 57 and 58: Годишник на Технич
- Page 59 and 60: Табл.11 2 3 4 5 6 7Загуби
- Page 61 and 62: оцени разхода на ак
- Page 63 and 64: сформатора се нала
- Page 65 and 66: -да допуска претова
- Page 67 and 68: Годишник на Технич
- Page 69 and 70: -големи трудности п
- Page 71 and 72: трансформаторът се
- Page 73 and 74: При известно фазов
- Page 75 and 76: KU BHOCHR (12)w w wЗа да се
- Page 77 and 78: Годишник на Технич
- Page 79 and 80: aided impregnation of wood and wood
- Page 81 and 82: different as a result of the differ
- Page 83 and 84: Table 2. Carbon peak C s1 component
- Page 85 and 86: Годишник на Технич
- Page 87 and 88: esults indicating that the reductio
- Page 89 and 90: Change of Mass M, %100-10-20-30-40
- Page 91 and 92: However, the correlation between re
- Page 93 and 94: Electrical Apparatus and Technologi
- Page 95 and 96: Годишник на Технич
- Page 97 and 98: - преходът към стри
- Page 99 and 100: или магнитно изоли
- Page 101 and 102: от лист електротех
- Page 103 and 104: Фиг. 6. Изменение на
- Page 105 and 106: Годишник на Технич
- Page 107: Fig.1 Block structure of proposed o
- Page 111 and 112: Fig.8 Calculated initial cogging to
- Page 113 and 114: Годишник на Технич
- Page 115 and 116: Octave/Lua interface is a Matlab to
- Page 117 and 118: pends on the results of the thermal
- Page 119 and 120: 4. ResultsAs it has been mentioned
- Page 121 and 122: A DC electromagnetic actuators with
- Page 123 and 124: Годишник на Технич
- Page 125 and 126: ращ се наблизо пров
- Page 127 and 128: Фиг. 4. Зависимост н
- Page 129 and 130: че максималната то
- Page 131 and 132: 3.7. Ефект близост в
- Page 133 and 134: Годишник на Технич
- Page 135 and 136: 11 c x6T 2 c3c4c5ec p c1c , (2)
- Page 137 and 138: От кривата на макси
- Page 139 and 140: 109.598.5Wind speed, m/s87.576.565.
- Page 141 and 142: 6. ЗаключениеВ стат
- Page 143 and 144: Годишник на Технич
- Page 145 and 146: Фиг.1. Заместваща сх
- Page 147 and 148: където t е времето м
- Page 149 and 150: Бяха проведени и ек
- Page 151 and 152: Представени са рез
- Page 153 and 154: Годишник на Технич
- Page 155 and 156: Фиг.3. Архитектури н
- Page 157 and 158: P SC_refP batP WP HGP storP bat_ref
- Page 159 and 160:
1500Фиг.9. Модел в Matlab/
- Page 161 and 162:
Isc, AVsc, V50403020100-10-20-30-40
- Page 163 and 164:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 165 and 166:
шаване на температ
- Page 167 and 168:
При променлив темп
- Page 169 and 170:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 171 and 172:
2. Примерни компютъ
- Page 173 and 174:
3.3. Изследване на фо
- Page 175 and 176:
алгебра. За целта с
- Page 177 and 178:
3.13. Изчисляване на
- Page 179 and 180:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 181 and 182:
Количеството на от
- Page 183 and 184:
(CaSO 4 .2H 2 O) (фиг. 3). То
- Page 185 and 186:
работят всички инс
- Page 187 and 188:
(НДНТ), което за Бъл
- Page 189 and 190:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 191 and 192:
Communications software and hardwar
- Page 193 and 194:
puter is running virtualization sof
- Page 195 and 196:
execution to the dispatcher applica
- Page 197 and 198:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 199 and 200:
Тунелирането скрив
- Page 201 and 202:
управление на ресу
- Page 203 and 204:
Фиг.6: Симулационен
- Page 205 and 206:
tunnel source 1.1.1.1tunnel destina
- Page 207 and 208:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 209 and 210:
При отворена вериг
- Page 211 and 212:
Таблица 3Задвижващ
- Page 213 and 214:
Фигура 3.При съотно
- Page 215 and 216:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 217 and 218:
Необходимо е така д
- Page 219 and 220:
yследователно:( k )UOsi
- Page 221 and 222:
Годишник на Технич
- Page 223 and 224:
Laskin and Wang presented a detaile
- Page 225 and 226:
Figure 2: Temperature dependence of
- Page 227 and 228:
An additional analysis obtained at