Landslides in the Sydney Basin - Geoscience Australia
Landslides in the Sydney Basin - Geoscience Australia
Landslides in the Sydney Basin - Geoscience Australia
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
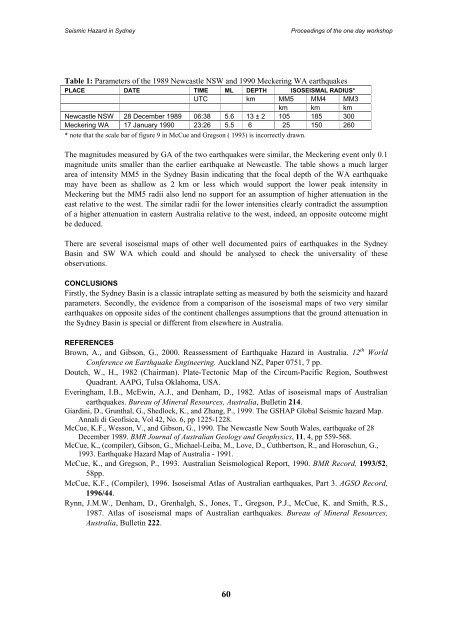
Seismic Hazard <strong>in</strong> <strong>Sydney</strong>Proceed<strong>in</strong>gs of <strong>the</strong> one day workshopTable 1: Parameters of <strong>the</strong> 1989 Newcastle NSW and 1990 Mecker<strong>in</strong>g WA earthquakesPLACE DATE TIME ML DEPTH ISOSEISMAL RADIUS*UTC km MM5 MM4 MM3km km kmNewcastle NSW 28 December 1989 06:38 5.6 13 ± 2 105 185 300Mecker<strong>in</strong>g WA 17 January 1990 23:26 5.5 6 25 150 260* note that <strong>the</strong> scale bar of figure 9 <strong>in</strong> McCue and Gregson ( 1993) is <strong>in</strong>correctly drawn.The magnitudes measured by GA of <strong>the</strong> two earthquakes were similar, <strong>the</strong> Mecker<strong>in</strong>g event only 0.1magnitude units smaller than <strong>the</strong> earlier earthquake at Newcastle. The table shows a much largerarea of <strong>in</strong>tensity MM5 <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Sydney</strong> Bas<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g that <strong>the</strong> focal depth of <strong>the</strong> WA earthquakemay have been as shallow as 2 km or less which would support <strong>the</strong> lower peak <strong>in</strong>tensity <strong>in</strong>Mecker<strong>in</strong>g but <strong>the</strong> MM5 radii also lend no support for an assumption of higher attenuation <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>east relative to <strong>the</strong> west. The similar radii for <strong>the</strong> lower <strong>in</strong>tensities clearly contradict <strong>the</strong> assumptionof a higher attenuation <strong>in</strong> eastern <strong>Australia</strong> relative to <strong>the</strong> west, <strong>in</strong>deed, an opposite outcome mightbe deduced.There are several isoseismal maps of o<strong>the</strong>r well documented pairs of earthquakes <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Sydney</strong>Bas<strong>in</strong> and SW WA which could and should be analysed to check <strong>the</strong> universality of <strong>the</strong>seobservations.CONCLUSIONSFirstly, <strong>the</strong> <strong>Sydney</strong> Bas<strong>in</strong> is a classic <strong>in</strong>traplate sett<strong>in</strong>g as measured by both <strong>the</strong> seismicity and hazardparameters. Secondly, <strong>the</strong> evidence from a comparison of <strong>the</strong> isoseismal maps of two very similarearthquakes on opposite sides of <strong>the</strong> cont<strong>in</strong>ent challenges assumptions that <strong>the</strong> ground attenuation <strong>in</strong><strong>the</strong> <strong>Sydney</strong> Bas<strong>in</strong> is special or different from elsewhere <strong>in</strong> <strong>Australia</strong>.REFERENCESBrown, A., and Gibson, G., 2000. Reassessment of Earthquake Hazard <strong>in</strong> <strong>Australia</strong>. 12 th WorldConference on Earthquake Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Auckland NZ, Paper 0751, 7 pp.Doutch, W., H., 1982 (Chairman). Plate-Tectonic Map of <strong>the</strong> Circum-Pacific Region, SouthwestQuadrant. AAPG, Tulsa Oklahoma, USA.Ever<strong>in</strong>gham, I.B., McEw<strong>in</strong>, A.J., and Denham, D., 1982. Atlas of isoseismal maps of <strong>Australia</strong>nearthquakes. Bureau of M<strong>in</strong>eral Resources, <strong>Australia</strong>, Bullet<strong>in</strong> 214.Giard<strong>in</strong>i, D., Grunthal, G., Shedlock, K., and Zhang, P., 1999. The GSHAP Global Seismic hazard Map.Annali di Geofisica, Vol 42, No. 6, pp 1225-1228.McCue, K.F., Wesson, V., and Gibson, G., 1990. The Newcastle New South Wales, earthquake of 28December 1989. BMR Journal of <strong>Australia</strong>n Geology and Geophysics, 11, 4, pp 559-568.McCue, K., (compiler), Gibson, G., Michael-Leiba, M., Love, D., Cuthbertson, R., and Horoschun, G.,1993. Earthquake Hazard Map of <strong>Australia</strong> - 1991.McCue, K., and Gregson, P., 1993. <strong>Australia</strong>n Seismological Report, 1990. BMR Record, 1993/52,58pp.McCue, K.F., (Compiler), 1996. Isoseismal Atlas of <strong>Australia</strong>n earthquakes, Part 3. AGSO Record,1996/44.Rynn, J.M.W., Denham, D., Grenhalgh, S., Jones, T., Gregson, P.J., McCue, K. and Smith, R.S.,1987. Atlas of isoseismal maps of <strong>Australia</strong>n earthquakes. Bureau of M<strong>in</strong>eral Resources,<strong>Australia</strong>, Bullet<strong>in</strong> 222.60