2019-20 N. American Planner_DP Sample
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
USEFUL INFORMATION<br />
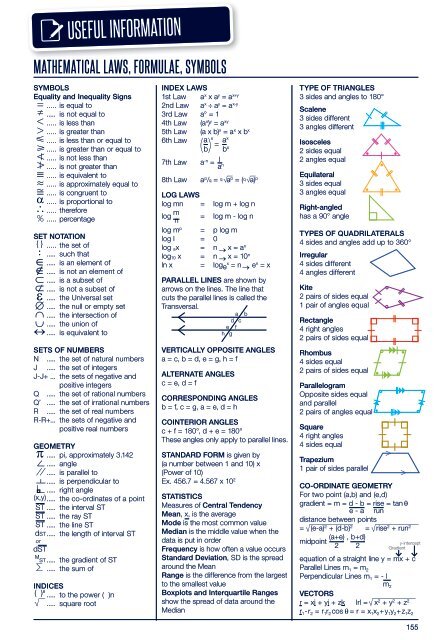
MATHEMATICAL LAWS, FORMULAE, SYMBOLS<br />
SYMBOLS<br />
Equality and Inequality Signs<br />
..... is equal to<br />
..... is not equal to<br />
..... is less than<br />
..... is greater than<br />
..... is less than or equal to<br />
..... is greater than or equal to<br />
..... is not less than<br />
..... is not greater than<br />
..... is equivalent to<br />
..... is approximately equal to<br />
..... is congruent to<br />
..... is proportional to<br />
..... therefore<br />
..... percentage<br />
SET NOTATION<br />
..... the set of<br />
..... such that<br />
..... is an element of<br />
..... is not an element of<br />
..... is a subset of<br />
..... is not a subset of<br />
..... the Universal set<br />
..... the null or empty set<br />
..... the intersection of<br />
..... the union of<br />
..... is equivalent to<br />
SETS OF NUMBERS<br />
N ..... the set of natural numbers<br />
J ..... the set of integers<br />
J-J+ ... the sets of negative and<br />
positive integers<br />
Q ..... the set of rational numbers<br />
Q’ ..... the set of irrational numbers<br />
R ..... the set of real numbers<br />
R-R+... the sets of negative and<br />
positive real numbers<br />
GEOMETRY<br />
..... pi, approximately 3.142<br />
..... angle<br />
..... is parallel to<br />
..... is perpendicular to<br />
..... right angle<br />
..... the co-ordinates of a point<br />
..... the interval ST<br />
..... the ray ST<br />
..... the line ST<br />
..... the length of interval ST<br />
or<br />
..... the gradient of ST<br />
..... the sum of<br />
INDICES<br />
..... to the power ( )n<br />
..... square root<br />
INDEX LAWS<br />
1st Law a x x a y = a x+y<br />
2nd Law a x a y = a x-y<br />
3rd Law a° = 1<br />
4th Law (a x ) y = a xy<br />
5th Law (a x b) x = a x x b x<br />
6th Law a x a x<br />
b = b x<br />
7th Law a -n =<br />
a l n<br />
8th Law a p /q = q a p = ( q a) p<br />
LOG LAWS<br />
log mn = log m + log n<br />
log m n<br />
= log m - log n<br />
log m p = p log m<br />
log l = 0<br />
log ax = n x = a n<br />
log 10 x = n x = 10 n<br />
ln x =<br />
x<br />
log e = n e n = x<br />
PARALLEL LINES are shown by<br />
arrows on the lines. The line that<br />
cuts the parallel lines is called the<br />
Transversal.<br />
a b<br />
d c<br />
e f<br />
h g<br />
VERTICALLY OPPOSITE ANGLES<br />
a = c, b = d, e = g, h = f<br />
ALTERNATE ANGLES<br />
c = e, d = f<br />
CORRESPONDING ANGLES<br />
b = f, c = g, a = e, d = h<br />
COINTERIOR ANGLES<br />
c + f = 180°, d + e = 180°<br />
These angles only apply to parallel lines.<br />
STANDARD FORM is given by<br />
(a number between 1 and 10) x<br />
(Power of 10)<br />
Ex. 456.7 = 4.567 x 10 2<br />
STATISTICS<br />
Measures of Central Tendency<br />
Mean, x, is the average<br />
Mode is the most common value<br />
Median is the middle value when the<br />
data is put in order<br />
Frequency is how often a value occurs<br />
Standard Deviation, SD is the spread<br />
around the Mean<br />
Range is the difference from the largest<br />
to the smallest value<br />
Boxplots and Interquartile Ranges<br />
show the spread of data around the<br />
Median<br />
TYPE OF TRIANGLES<br />
3 sides and angles to 180°<br />
Scalene<br />
3 sides different<br />
3 angles different<br />
Isosceles<br />
2 sides equal<br />
2 angles equal<br />
Equilateral<br />
3 sides equal<br />
3 angles equal<br />
Right-angled<br />
has a 90° angle<br />
TYPES OF QUADRILATERALS<br />
4 sides and angles add up to 360°<br />
Irregular<br />
4 sides different<br />
4 angles different<br />
Kite<br />
2 pairs of sides equal<br />
1 pair of angles equal<br />
Rectangle<br />
4 right angles<br />
2 pairs of sides equal<br />
Rhombus<br />
4 sides equal<br />
2 pairs of sides equal<br />
Parallelogram<br />
Opposite sides equal<br />
and parallel<br />
2 pairs of angles equal<br />
Square<br />
4 right angles<br />
4 sides equal<br />
Trapezium<br />
1 pair of sides parallel<br />
CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY<br />
For two point (a,b) and (e,d)<br />
gradient = m = d - b = rise = tan<br />
e - a run<br />
distance between points<br />
= (e-a) 2 + (d-b) 2 = rise 2 + run 2<br />
midpoint<br />
(a+e) , b+d)<br />
2 2<br />
y-intercept<br />
Gradient<br />
equation of a straight line y = mx + c<br />
Parallel Lines m 1 = m 2<br />
Perpendicular Lines m 1 = - l<br />
m 2<br />
VECTORS<br />
r = xi + yi + zk lrl = x 2 + y 2 + z 2<br />
r 1 -r 2 = r 1 r 2 cos = r = x 1 x 2 +y 1 y 2 +z 1 z 2<br />
155<br />
<strong>20</strong>18/19 Intl <strong>Planner</strong>_<strong>DP</strong>_REAR.indd 155 25/5/18 3:15 pm