The Earliest Inhabitants: The Dynamics of the Jamaican Taino
by Lesley-Gail Atkinson
by Lesley-Gail Atkinson
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Howard (1965) recognized that Redware pottery was similar to <strong>the</strong><br />
Ostionoid pottery described by Rouse. <strong>Jamaican</strong> Redware, however, is different<br />
from Ostionoid pottery found elsewhere in <strong>the</strong> Greater Antilles; for that<br />
reason he named <strong>the</strong> style after <strong>the</strong> Little River site (though many people continue<br />
to use <strong>the</strong> name Redware to describe this style). Howard noted that<br />
<strong>the</strong>re was ano<strong>the</strong>r kind <strong>of</strong> pottery decorated with incised designs and filleted<br />
rims that was very similar to <strong>the</strong> Meillacoid pottery from Hispaniola, and he<br />
called this style White Marl after <strong>the</strong> site at which it was first described.<br />
Howard (ibid.) recognized that <strong>the</strong> pottery from <strong>the</strong> Fairfield site near<br />
Montego Bay was similar to White Marl pottery, but that it was also quite<br />
distinctive. He <strong>the</strong>refore identified <strong>the</strong> Fairfield complex or <strong>the</strong> Montego<br />
Bay style, which characterized <strong>the</strong> pottery <strong>of</strong> northwestern Jamaica. 2<br />
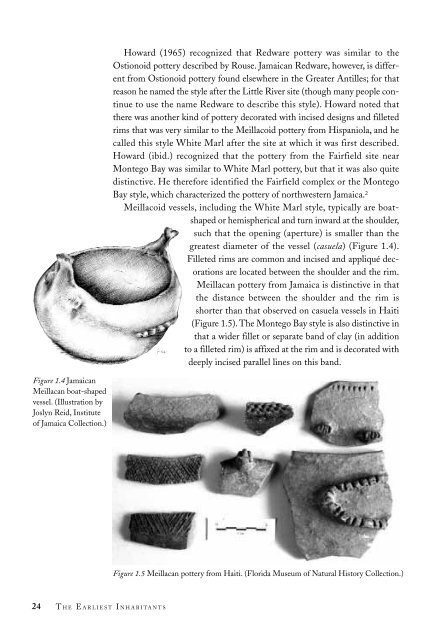
Meillacoid vessels, including <strong>the</strong> White Marl style, typically are boatshaped<br />
or hemispherical and turn inward at <strong>the</strong> shoulder,<br />
such that <strong>the</strong> opening (aperture) is smaller than <strong>the</strong><br />
greatest diameter <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> vessel (casuela) (Figure 1.4).<br />
Filleted rims are common and incised and appliqué decorations<br />
are located between <strong>the</strong> shoulder and <strong>the</strong> rim.<br />
Meillacan pottery from Jamaica is distinctive in that<br />
<strong>the</strong> distance between <strong>the</strong> shoulder and <strong>the</strong> rim is<br />
shorter than that observed on casuela vessels in Haiti<br />
(Figure 1.5). <strong>The</strong> Montego Bay style is also distinctive in<br />
that a wider fillet or separate band <strong>of</strong> clay (in addition<br />
to a filleted rim) is affixed at <strong>the</strong> rim and is decorated with<br />
deeply incised parallel lines on this band.<br />
Figure 1.4 <strong>Jamaican</strong><br />
Meillacan boat-shaped<br />
vessel. (Illustration by<br />
Joslyn Reid, Institute<br />
<strong>of</strong> Jamaica Collection.)<br />
Figure 1.5 Meillacan pottery from Haiti. (Florida Museum <strong>of</strong> Natural History Collection.)<br />
24 T HE E ARLIEST I NHABITANTS