Caring for Pollinators - Bundesamt für Naturschutz
Caring for Pollinators - Bundesamt für Naturschutz
Caring for Pollinators - Bundesamt für Naturschutz
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Steffan-Dewenter Pollinator declines and loss of pollination services<br />
Drivers of pollinator loss<br />
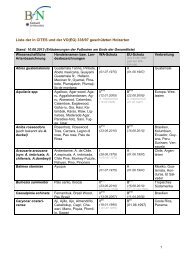
Several case studies identify habitat fragmentation and land use intensification as important<br />
drivers of pollinator declines (Figure 3). The reduction of habitat area and the increase of<br />
habitat isolation lead to lower species richness and abundance and shifts in community<br />
composition. Particularly food plant specialists, cuckoo bees and small, solitary bee species<br />
are affected by habitat fragmentation (Steffan-Dewenter & Westphal 2008). Interestingly, not<br />
only local habitat characteristics but also the management of the wider landscape play a vital<br />
role <strong>for</strong> pollinator diversity. Thus the implementation of adequate agri-environmental<br />
schemes could contribute to the conservation of pollinators in agricultural landscapes<br />
(Steffan-Dewenter & Westphal 2008, Meyer et al. 2008). The functional consequences of<br />
pollinator declines <strong>for</strong> pollination of rare plants and crops are a controversially discussed and<br />
still unsolved research question.<br />
Fig. 3: The interplay of<br />
pollination services, pollinators,<br />
habitat fragmentation and land<br />
use intensification (from Steffan-<br />
Dewenter & Westphal 2008)<br />
Consequences of pollinator declines <strong>for</strong> rare plant pollination<br />
In the framework of the EU-project ALARM we developed a common study design and<br />
protocols to evaluate the importance of population size, patch size and plant density on<br />
flower visitation, pollinator diversity, and fruit or seed set. The research was per<strong>for</strong>med in 5<br />
European countries with altogether 10 focal rare plant species. The results show no effect of<br />
overall population size but significant effects of patch area and patch density on flower<br />
visitation rates and seed set. For five out of 10 plant species the data provide evidence <strong>for</strong><br />
significant pollination limitation (Dauber et al., submitted).<br />
103