Research Publications - College of Medicine and Health Science
Research Publications - College of Medicine and Health Science
Research Publications - College of Medicine and Health Science
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
mice for a better immune response to infection.<br />
We are currently analyzing the functional link<br />
between the nervous <strong>and</strong> immune systems.<br />
Another area <strong>of</strong> interest, in which my laboratory<br />
is working, is the expression <strong>of</strong> different biomarkers<br />
in cancer cells. We are leading a project in<br />
which we are trying to correlate the expression<br />
<strong>of</strong> an intracellular protein (MCJ) in breast cancer<br />
cells with their resistance to chemotherapy.<br />
<strong>Research</strong> Highlights<br />
Our research had shown that the inhibition <strong>of</strong><br />
�������������<br />
�����<br />
�����<br />
�����<br />
����<br />
����<br />
���������<br />
����������� �����<br />
����<br />
��������<br />
����<br />
Signal transduction pathways <strong>and</strong> disease<br />
(Pr<strong>of</strong>. Sehamuddin Galadari)<br />
Biologically active sphingolipids have key<br />
roles in the regulation <strong>of</strong> several fundamental<br />
biological processes that are integral to cancer<br />
pathogenesis. Recent significant progress in<br />
underst<strong>and</strong>ing biologically active sphingolipid<br />
synthesis, specifically within ceramide, sphingosine<br />
<strong>and</strong> sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)mediated<br />
pathways, has identified crucial roles<br />
for these molecules both in cancer development<br />
the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which<br />
leads to an accumulation <strong>of</strong> acetylcholine<br />
(ACh), enabled mice to mount a more effective<br />
inflammatory antimicrobial response. Immunologically,<br />
inhibition <strong>of</strong> AChE, can modulate the<br />
inflammatory response <strong>of</strong> splenic macrophages<br />
<strong>and</strong> enhance the antibody response to infection<br />
in these animals. Moreover, preliminary results<br />
suggest that AChE inhibition could also modulate<br />
macrophage inflammatory responses, both<br />
in infections as well as non-infections disease<br />
models.<br />
���������<br />
�����<br />
����������<br />
�������<br />
��������������������<br />
�������������<br />
��������<br />
���������<br />
�����<br />
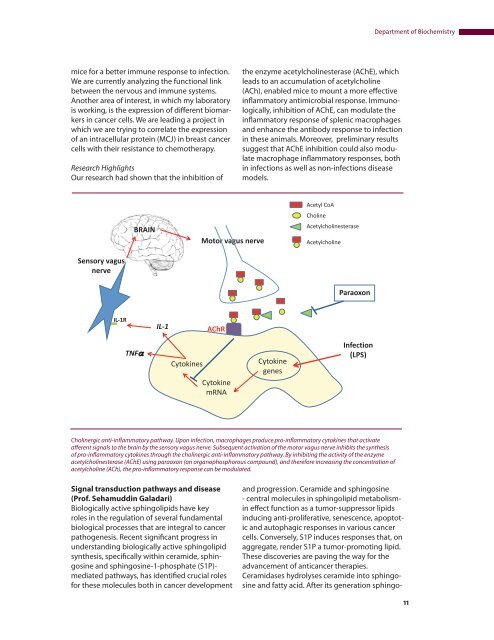
Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Upon infection, macrophages produce pro-inflammatory cytokines that activate<br />
afferent signals to the brain by the sensory vagus nerve. Subsequent activation <strong>of</strong> the motor vagus nerve inhibits the synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> pro-inflammatory cytokines through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. By inhibiting the activity <strong>of</strong> the enzyme<br />
acetylcholinesterase (AChE) using paraoxon (an organophosphorous compound), <strong>and</strong> therefore increasing the concentration <strong>of</strong><br />
acetylcholine (ACh), the pro-inflammatory response can be modulated.<br />
<strong>and</strong> progression. Ceramide <strong>and</strong> sphingosine<br />
- central molecules in sphingolipid metabolism-<br />
in effect function as a tumor-suppressor lipids<br />
inducing anti-proliferative, senescence, apoptotic<br />
<strong>and</strong> autophagic responses in various cancer<br />
cells. Conversely, S1P induces responses that, on<br />
aggregate, render S1P a tumor-promoting lipid.<br />
These discoveries are paving the way for the<br />
advancement <strong>of</strong> anticancer therapies.<br />
Ceramidases hydrolyses ceramide into sphingosine<br />
<strong>and</strong> fatty acid. After its generation sphingo-<br />
Department <strong>of</strong> Biochemistry<br />
�<br />
11