la teoria di Rankine
la teoria di Rankine
la teoria di Rankine
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
UNIVERSITA’ DEGLI STUDI DI FIRENZE<br />
DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA CIVILE<br />
Sezione geotecnica<br />
Teoria <strong>di</strong> <strong>Rankine</strong><br />
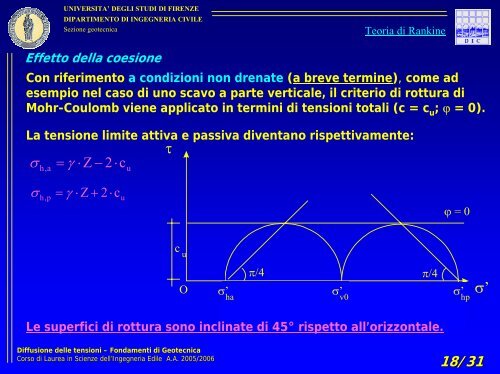
Effetto del<strong>la</strong> coesione<br />
Con riferimento a con<strong>di</strong>zioni non drenate (a breve termine), come ad<br />
esempio nel caso <strong>di</strong> uno scavo a parte verticale, il criterio <strong>di</strong> rottura <strong>di</strong><br />
Mohr-Coulomb viene applicato in termini <strong>di</strong> tensioni totali (c = c u<br />
; ϕ = 0).<br />
La tensione limite attiva e passiva <strong>di</strong>ventano rispettivamente:<br />
σ<br />
h,a<br />
= γ ⋅<br />
Z − 2⋅c<br />
u<br />
τ<br />
σ<br />
h,p<br />
= γ ⋅<br />
Z + 2⋅c<br />
u<br />
ϕ = 0<br />
c<br />
u<br />
π/4 π/4<br />
O σ’ σ’<br />
σ’<br />
ha ha<br />
v0<br />
σ’ hp<br />
σ’<br />
Le superfici <strong>di</strong> rottura sono inclinate <strong>di</strong> 45° rispetto all’orizzontale.<br />
Diffusione delle tensioni – Fondamenti <strong>di</strong> Geotecnica<br />
Corso <strong>di</strong> Laurea in Scienze dell’Ingegneria E<strong>di</strong>le A.A. 2005/2006 18/31