Aanesthetic Agents for Day Surgery - NIHR Health Technology ...
Aanesthetic Agents for Day Surgery - NIHR Health Technology ...
Aanesthetic Agents for Day Surgery - NIHR Health Technology ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
with respect to late recovery in any study.<br />
Psychomotor recovery after desflurane was faster<br />
than after sevoflurane in the absence of N 2O,<br />
but in those patients who received N 2O there<br />
was no difference.<br />
Isoflurane and desflurane<br />
These agents were compared in three studies, 79,95,223<br />
all of which used propofol <strong>for</strong> induction. Gupta<br />
and co-workers 79 and Rieker 226 added either<br />
fentanyl or alfentanil. A fourth study 73 used<br />
thiopentone <strong>for</strong> induction, with no opioid. In all<br />
cases desflurane was better than isoflurane with<br />
respect to early and intermediate recovery, but<br />
there was no difference between the agents with<br />
respect to later recovery. In the patients who had<br />
received propofol <strong>for</strong> induction, psychomotor<br />
recovery was better after desflurane than after<br />
isoflurane, although there was no difference<br />
between the two agents when thiopentone<br />
was used <strong>for</strong> induction.<br />
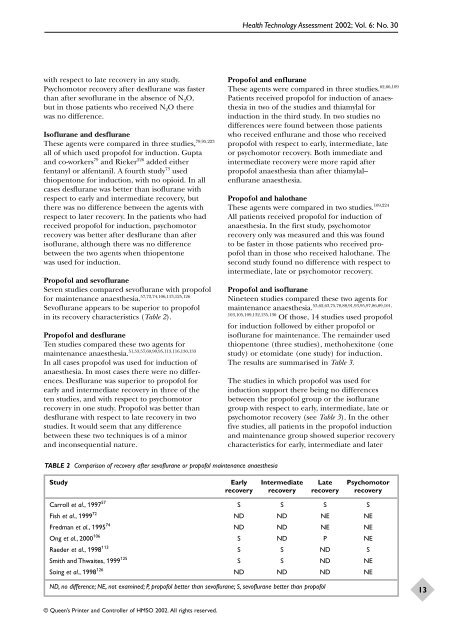
Propofol and sevoflurane<br />
Seven studies compared sevoflurane with propofol<br />
<strong>for</strong> maintenance anaesthesia. 57,72,74,106,113,125,126<br />
Sevoflurane appears to be superior to propofol<br />
in its recovery characteristics (Table 2).<br />
Propofol and desflurane<br />
Ten studies compared these two agents <strong>for</strong><br />
maintenance anaesthesia. 51,53,57,69,90,95,113,116,130,133<br />
In all cases propofol was used <strong>for</strong> induction of<br />
anaesthesia. In most cases there were no differences.<br />
Desflurane was superior to propofol <strong>for</strong><br />
early and intermediate recovery in three of the<br />
ten studies, and with respect to psychomotor<br />
recovery in one study. Propofol was better than<br />
desflurane with respect to late recovery in two<br />
studies. It would seem that any difference<br />
between these two techniques is of a minor<br />
and inconsequential nature.<br />
TABLE 2 Comparison of recovery after sevoflurane or propofol maintenance anaesthesia<br />
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2002. All rights reserved.<br />
<strong>Health</strong> <strong>Technology</strong> Assessment 2002; Vol. 6: No. 30<br />
Propofol and enflurane<br />
These agents were compared in three studies. 62,66,109<br />
Patients received propofol <strong>for</strong> induction of anaesthesia<br />
in two of the studies and thiamylal <strong>for</strong><br />
induction in the third study. In two studies no<br />
differences were found between those patients<br />
who received enflurane and those who received<br />
propofol with respect to early, intermediate, late<br />
or psychomotor recovery. Both immediate and<br />
intermediate recovery were more rapid after<br />
propofol anaesthesia than after thiamylal–<br />
enflurane anaesthesia.<br />
Propofol and halothane<br />
These agents were compared in two studies. 109,224<br />
All patients received propofol <strong>for</strong> induction of<br />
anaesthesia. In the first study, psychomotor<br />
recovery only was measured and this was found<br />
to be faster in those patients who received propofol<br />
than in those who received halothane. The<br />
second study found no difference with respect to<br />
intermediate, late or psychomotor recovery.<br />
Propofol and isoflurane<br />
Nineteen studies compared these two agents <strong>for</strong><br />
maintenance anaesthesia. 53,62,63,75,78,88,91,93,95,97,86,89,101,<br />
103,105,109,132,135,136 Of those, 14 studies used propofol<br />
<strong>for</strong> induction followed by either propofol or<br />
isoflurane <strong>for</strong> maintenance. The remainder used<br />
thiopentone (three studies), methohexitone (one<br />
study) or etomidate (one study) <strong>for</strong> induction.<br />
The results are summarised in Table 3.<br />
The studies in which propofol was used <strong>for</strong><br />
induction support there being no differences<br />
between the propofol group or the isoflurane<br />
group with respect to early, intermediate, late or<br />
psychomotor recovery (see Table 3). In the other<br />
five studies, all patients in the propofol induction<br />
and maintenance group showed superior recovery<br />
characteristics <strong>for</strong> early, intermediate and later<br />
Study Early Intermediate Late Psychomotor<br />
recovery recovery recovery recovery<br />
Carroll et al., 1997 57<br />
Fish et al., 1999 72<br />
Fredman et al., 1995 74<br />
Ong et al., 2000 106<br />
Raeder et al., 1998 113<br />
Smith and Thwaites, 1999 125<br />
Soing et al., 1998 126<br />
S S S S<br />
ND ND NE NE<br />
ND ND NE NE<br />
S ND P NE<br />
S S ND S<br />
S S ND NE<br />
ND ND ND NE<br />
ND, no difference; NE, not examined; P, propofol better than sevoflurane; S, sevoflurane better than propofol<br />
13