Livelihood Security: Climate change, conflict and migration in - UNEP
Livelihood Security: Climate change, conflict and migration in - UNEP
Livelihood Security: Climate change, conflict and migration in - UNEP
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
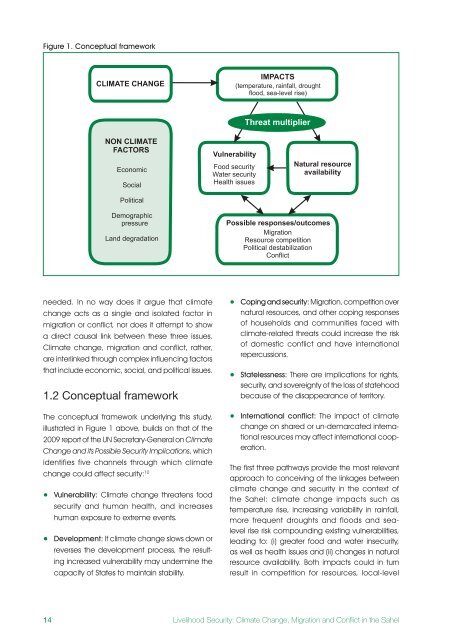
Figure 1 . Conceptual framework<br />
needed. In no way does it argue that climate<br />
<strong>change</strong> acts as a s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>and</strong> isolated factor <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>migration</strong> or <strong>conflict</strong>, nor does it attempt to show<br />
a direct causal l<strong>in</strong>k between these three issues.<br />
<strong>Climate</strong> <strong>change</strong>, <strong>migration</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>conflict</strong>, rather,<br />
are <strong>in</strong>terl<strong>in</strong>ked through complex <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g factors<br />
that <strong>in</strong>clude economic, social, <strong>and</strong> political issues.<br />
1.2 Conceptual framework<br />
The conceptual framework underly<strong>in</strong>g this study,<br />
illustrated <strong>in</strong> Figure 1 above, builds on that of the<br />
2009 report of the UN Secretary-General on <strong>Climate</strong><br />
Change <strong>and</strong> its Possible <strong>Security</strong> Implications, which<br />
identifies five channels through which climate<br />
<strong>change</strong> could affect security: 10<br />
•<br />
•<br />
14<br />
CLIMATE CHANGE<br />
NON CLIMATE<br />
FACTORS<br />
Economic<br />
Social<br />
Political<br />
Demographic<br />
pressure<br />
L<strong>and</strong> degradation<br />
Vulnerability: <strong>Climate</strong> <strong>change</strong> threatens food<br />
security <strong>and</strong> human health, <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>creases<br />
human exposure to extreme events.<br />
Development: If climate <strong>change</strong> slows down or<br />
reverses the development process, the result<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>creased vulnerability may underm<strong>in</strong>e the<br />
capacity of States to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> stability.<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
IMPACTS<br />
(temperature, ra<strong>in</strong>fall, drought<br />
flood, sea-level rise)<br />
Vulnerability<br />
Food security<br />
Water security<br />
Health issues<br />
Threat multiplier<br />
Natural resource<br />
availability<br />
Possible responses/outcomes<br />
Migration<br />
Resource competition<br />
Political destabilization<br />
Conflict<br />
Cop<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> security: Migration, competition over<br />
natural resources, <strong>and</strong> other cop<strong>in</strong>g responses<br />
of households <strong>and</strong> communities faced with<br />
climate-related threats could <strong>in</strong>crease the risk<br />
of domestic <strong>conflict</strong> <strong>and</strong> have <strong>in</strong>ternational<br />
repercussions.<br />
Statelessness: There are implications for rights,<br />
security, <strong>and</strong> sovereignty of the loss of statehood<br />
because of the disappearance of territory.<br />
International <strong>conflict</strong>: The impact of climate<br />
<strong>change</strong> on shared or un-demarcated <strong>in</strong>ternational<br />
resources may affect <strong>in</strong>ternational cooperation.<br />
The first three pathways provide the most relevant<br />
approach to conceiv<strong>in</strong>g of the l<strong>in</strong>kages between<br />
climate <strong>change</strong> <strong>and</strong> security <strong>in</strong> the context of<br />
the Sahel: climate <strong>change</strong> impacts such as<br />
temperature rise, <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g variability <strong>in</strong> ra<strong>in</strong>fall,<br />
more frequent droughts <strong>and</strong> floods <strong>and</strong> sealevel<br />
rise risk compound<strong>in</strong>g exist<strong>in</strong>g vulnerabilities,<br />
lead<strong>in</strong>g to: (i) greater food <strong>and</strong> water <strong>in</strong>security,<br />
as well as health issues <strong>and</strong> (ii) <strong>change</strong>s <strong>in</strong> natural<br />
resource availability. Both impacts could <strong>in</strong> turn<br />
result <strong>in</strong> competition for resources, local-level<br />
<strong>Livelihood</strong> <strong>Security</strong>: <strong>Climate</strong> Change, Migration <strong>and</strong> Conflict <strong>in</strong> the Sahel