A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and ...
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and ...
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
94<br />
Review <strong>of</strong> <strong>economic</strong> evaluations <strong>of</strong> ADHD drug interventions in children <strong>and</strong> adolescents<br />
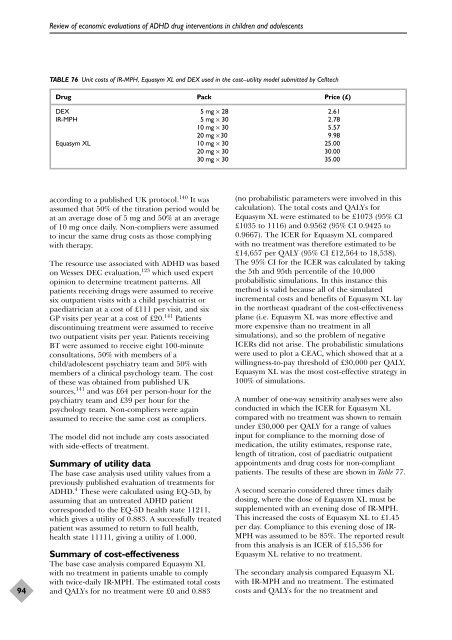
TABLE 76 Unit costs <strong>of</strong> IR-MPH, Equasym XL <strong>and</strong> DEX used in <strong>the</strong> cost–utility <strong>model</strong> submitted by Celltech<br />
Drug Pack Price (£)<br />
DEX 5 mg × 28 2.61<br />
IR-MPH 5 mg × 30 2.78<br />
10 mg × 30 5.57<br />
20 mg × 30 9.98<br />
Equasym XL 10 mg × 30 25.00<br />
20 mg × 30 30.00<br />
30 mg × 30 35.00<br />
according to a published UK protocol. 140 It was<br />
assumed that 50% <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> titration period would be<br />
at an average dose <strong>of</strong> 5 mg <strong>and</strong> 50% at an average<br />
<strong>of</strong> 10 mg once daily. Non-compliers were assumed<br />
to incur <strong>the</strong> same drug costs as those complying<br />
with <strong>the</strong>rapy.<br />
The resource use associated with ADHD was based<br />
on Wessex DEC evaluation, 123 which used expert<br />
opinion to determine treatment patterns. All<br />
patients receiving drugs were assumed to receive<br />
six outpatient visits with a child psychiatrist or<br />
paediatrician at a cost <strong>of</strong> £111 per visit, <strong>and</strong> six<br />
GP visits per year at a cost <strong>of</strong> £20. 141 Patients<br />
discontinuing treatment were assumed to receive<br />
two outpatient visits per year. Patients receiving<br />
BT were assumed to receive eight 100-minute<br />
consultations, 50% with members <strong>of</strong> a<br />
child/adolescent psychiatry team <strong>and</strong> 50% with<br />
members <strong>of</strong> a clinical psychology team. The cost<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se was obtained from published UK<br />
sources, 141 <strong>and</strong> was £64 per person-hour for <strong>the</strong><br />
psychiatry team <strong>and</strong> £39 per hour for <strong>the</strong><br />
psychology team. Non-compliers were again<br />
assumed to receive <strong>the</strong> same cost as compliers.<br />
The <strong>model</strong> did not include any costs associated<br />
with side-effects <strong>of</strong> treatment.<br />
Summary <strong>of</strong> utility data<br />
The base case analysis used utility values from a<br />
previously published evaluation <strong>of</strong> treatments for<br />
ADHD. 4 These were calculated using EQ-5D, by<br />
assuming that an untreated ADHD patient<br />
corresponded to <strong>the</strong> EQ-5D health state 11211,<br />
which gives a utility <strong>of</strong> 0.883. A successfully treated<br />
patient was assumed to return to full health,<br />
health state 11111, giving a utility <strong>of</strong> 1.000.<br />
Summary <strong>of</strong> cost-<strong>effectiveness</strong><br />
The base case analysis compared Equasym XL<br />
with no treatment in patients unable to comply<br />
with twice-daily IR-MPH. The estimated total costs<br />
<strong>and</strong> QALYs for no treatment were £0 <strong>and</strong> 0.883<br />
(no probabilistic parameters were involved in this<br />
calculation). The total costs <strong>and</strong> QALYs for<br />
Equasym XL were estimated to be £1073 (95% CI<br />
£1035 to 1116) <strong>and</strong> 0.9562 (95% CI 0.9425 to<br />
0.9667). The ICER for Equasym XL compared<br />
with no treatment was <strong>the</strong>refore estimated to be<br />
£14,657 per QALY (95% CI £12,564 to 18,538).<br />
The 95% CI for <strong>the</strong> ICER was calculated by taking<br />
<strong>the</strong> 5th <strong>and</strong> 95th percentile <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 10,000<br />
probabilistic simulations. In this instance this<br />
method is valid because all <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> simulated<br />
incremental costs <strong>and</strong> benefits <strong>of</strong> Equasym XL lay<br />
in <strong>the</strong> nor<strong>the</strong>ast quadrant <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> cost-<strong>effectiveness</strong><br />
plane (i.e. Equasym XL was more effective <strong>and</strong><br />
more expensive than no treatment in all<br />
simulations), <strong>and</strong> so <strong>the</strong> problem <strong>of</strong> negative<br />
ICERs did not arise. The probabilistic simulations<br />
were used to plot a CEAC, which showed that at a<br />
willingness-to-pay threshold <strong>of</strong> £30,000 per QALY,<br />
Equasym XL was <strong>the</strong> most cost-effective strategy in<br />
100% <strong>of</strong> simulations.<br />
A number <strong>of</strong> one-way sensitivity analyses were also<br />
conducted in which <strong>the</strong> ICER for Equasym XL<br />
compared with no treatment was shown to remain<br />
under £30,000 per QALY for a range <strong>of</strong> values<br />
input for compliance to <strong>the</strong> morning dose <strong>of</strong><br />
medication, <strong>the</strong> utility estimates, response rate,<br />
length <strong>of</strong> titration, cost <strong>of</strong> paediatric outpatient<br />
appointments <strong>and</strong> drug costs for non-compliant<br />
patients. The results <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se are shown in Table 77.<br />
A second scenario considered three times daily<br />
dosing, where <strong>the</strong> dose <strong>of</strong> Equasym XL must be<br />
supplemented with an evening dose <strong>of</strong> IR-MPH.<br />
This increased <strong>the</strong> costs <strong>of</strong> Equasym XL to £1.45<br />
per day. Compliance to this evening dose <strong>of</strong> IR-<br />
MPH was assumed to be 85%. The reported result<br />
from this analysis is an ICER <strong>of</strong> £15,536 for<br />
Equasym XL relative to no treatment.<br />
The secondary analysis compared Equasym XL<br />
with IR-MPH <strong>and</strong> no treatment. The estimated<br />
costs <strong>and</strong> QALYs for <strong>the</strong> no treatment <strong>and</strong>