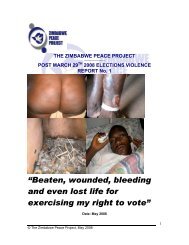
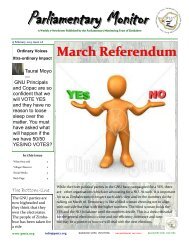
Moving forward in Zimbabwe - Brooks World Poverty Institute - The ...
Moving forward in Zimbabwe - Brooks World Poverty Institute - The ...
Moving forward in Zimbabwe - Brooks World Poverty Institute - The ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Mov<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>forward</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Zimbabwe</strong><br />
Reduc<strong>in</strong>g poverty and promot<strong>in</strong>g growth<br />
Figure 7.1: Crude death rate trends, 1980-2007.<br />
Source: GoZ, 2008.<br />
Figure 7.1 shows the deterioration <strong>in</strong> <strong>Zimbabwe</strong>’s health status.<br />
After <strong>in</strong>itial improvements dur<strong>in</strong>g the 1980’s, from the early 1990s<br />
crude death rates rose as the impact of HIV/AIDS mortality and<br />
cuts <strong>in</strong> public health expenditure began to affect health delivery.<br />
<strong>The</strong> crude death rate dropped from 10.8 <strong>in</strong> 1982 to 6.1 <strong>in</strong> 1987,<br />
then rose to 9.49 <strong>in</strong> 1992 before nearly doubl<strong>in</strong>g to 17.2/1,000<br />
population <strong>in</strong> 2007. Similarly <strong>in</strong>fant mortality that had decl<strong>in</strong>ed to<br />
53 per 1,000 live birth had risen to 68 per 1,000 by 2008. Although<br />
this is nowhere near the rates reached by other countries emerg<strong>in</strong>g<br />
from conflict (for example, Sierra Leone had rates of 170 per<br />
1,000 at the end of the war <strong>in</strong> 1999 while rates <strong>in</strong> Mozambique had<br />
reached 269 per 1,000 by the time the civil war ended <strong>in</strong> 1991 3 ) it is<br />
the reversal of ga<strong>in</strong>s that is worry<strong>in</strong>g here. A look at life expectancy<br />
at birth reflected <strong>in</strong> Table 7.4 also shows a dramatic decl<strong>in</strong>e from<br />
62 <strong>in</strong> 1990 to the current 43 years.<br />
Most of this decl<strong>in</strong>e has been attributed to the HIV/AIDS<br />
epidemic and deterioration <strong>in</strong> health services programm<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
delivery. <strong>Zimbabwe</strong> is one of the countries hardest hit by the HIV/<br />
AIDS epidemic. Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> this area cont<strong>in</strong>ued ma<strong>in</strong>ly due to<br />
dedicated fund<strong>in</strong>g from a government levy and also donor support.<br />
Figure 7.2 shows trends <strong>in</strong> the adult prevalence and <strong>in</strong>cidence of<br />
HIV/AIDS between 1980 and 2007.<br />
Table 7.4: Life expectancy at birth, 1984-2006.<br />
1984 1986 1988 1990 1995 2000 2002 2006<br />
Male 60 61 61 58 52.6 44 43 44<br />
Female 61 61 63 65 57.2 46 46 43<br />
Total 60 61 62 62 55 45 45 43<br />
Source: <strong>Zimbabwe</strong> Inter-Censal Demographic Survey (ZICDS),<br />
CSO <strong>World</strong> Health statistics.<br />
Figure 7.2 shows an impressive decl<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> prevalence rates<br />
from 24.5 per cent <strong>in</strong> 2004 to 15.6 per cent by 2007. <strong>The</strong> <strong>in</strong>cidence<br />
rate is also down to two per cent from a peak well above four per<br />
cent <strong>in</strong> the mid 1990s. Success <strong>in</strong> tackl<strong>in</strong>g HIV/AIDS has been<br />
due to a comb<strong>in</strong>ation of behaviour change, migration and the<br />
economic situation. Most significant, however, is the fact that this<br />
is one of the few areas where cont<strong>in</strong>ued long-term programm<strong>in</strong>g<br />
has been ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>ed through dedicated fund<strong>in</strong>g from the state<br />
and considerable donor support. It is partly this susta<strong>in</strong>ed and coord<strong>in</strong>ated<br />
effort that has delivered the decl<strong>in</strong>e.<br />
Figure 7.2: Trends <strong>in</strong> HIV and AIDS prevalence and <strong>in</strong>cidence, 1980-2007.<br />
Source: GoZ, 2008.<br />
89