You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
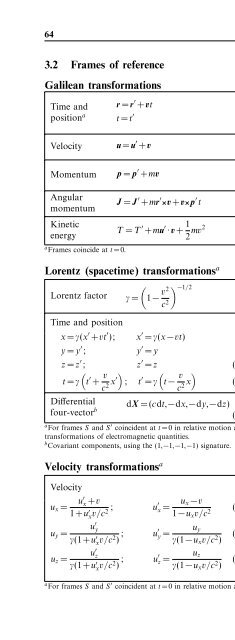
64 Dynamics and mechanics<br />
3.2 Frames <strong>of</strong> reference<br />
Galilean transformations<br />
Time and<br />
position a<br />
r = r ′ +vt (3.1)<br />
t = t ′ (3.2)<br />
r,r ′<br />
position in frames S<br />
and S ′<br />
v velocity <strong>of</strong> S ′ in S<br />
t,t ′ time in S and S ′<br />
Velocity u = u ′ +v (3.3) u,u ′ velocity in frames S<br />
and S ′<br />
Momentum p = p ′ +mv (3.4)<br />
Angular<br />
momentum<br />
Kinetic<br />
energy<br />
a Frames coincide at t =0.<br />
p,p ′<br />
m<br />
particle momentum<br />
in frames S and S ′<br />
particle mass<br />
J = J ′ +mr ′ ×v +v×p ′ t (3.5) J ,J ′ angular momentum<br />
in frames S and S ′<br />
T = T ′ +mu ′ ·v + 1 2 mv2 (3.6)<br />
T,T ′<br />
kinetic energy in<br />
frames S and S ′<br />
S<br />
vt<br />
S ′<br />
r<br />
r ′<br />
m<br />
Lorentz (spacetime) transformations a<br />
Lorentz factor<br />
) −1/2<br />
γ =<br />
(1− v2<br />
c 2 (3.7)<br />
γ<br />
v<br />
c<br />
Lorentz factor<br />
velocity <strong>of</strong> S ′ in S<br />
speed <strong>of</strong> light<br />
Time and position<br />
x = γ(x ′ +vt ′ ); x ′ = γ(x−vt) (3.8)<br />
y = y ′ ; y ′ = y (3.9)<br />
z = z ′ ; z ′ = z (3.10)<br />
(<br />
t = γ t ′ + v c 2 x′) ; t ′ = γ<br />
(t− v )<br />
c 2 x (3.11)<br />
x,x ′<br />
t,t ′<br />
x-position in frames<br />
S and S ′ (similarly<br />
for y and z)<br />
time in frames S and<br />
S ′<br />
S S ′ v<br />
x x ′<br />
Differential<br />
four-vector b<br />
dX =(cdt,−dx,−dy,−dz)<br />
(3.12)<br />
X<br />
spacetime four-vector<br />
a For frames S and S ′ coincident at t = 0 in relative motion along x. See page 141 for the<br />
transformations <strong>of</strong> electromagnetic quantities.<br />
b Covariant components, using the (1,−1,−1,−1) signature.<br />
Velocity transformations a<br />
Velocity<br />
u x = u′ x +v<br />
1+u ′ xv/c 2 ; u′ x = u x −v<br />
1−u x v/c 2 (3.13)<br />
u ′ y<br />
u y =<br />
γ(1+u ′ xv/c 2 ) ; u y<br />
u′ y =<br />
γ(1−u x v/c 2 )<br />
(3.14)<br />
u ′ z<br />
u z =<br />
γ(1+u ′ xv/c 2 ) ; u z<br />
u′ z =<br />
γ(1−u x v/c 2 )<br />
(3.15)<br />
γ<br />
v<br />
c<br />
u i ,u ′ i<br />
Lorentz factor<br />
=[1−(v/c) 2 ] −1/2<br />
velocity <strong>of</strong> S ′ in S<br />
speed <strong>of</strong> light<br />
particle velocity<br />
components in<br />
frames S and S ′<br />
S S ′ u<br />
v<br />
x x ′<br />
a For frames S and S ′ coincident at t = 0 in relative motion along x.