- Page 2:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 8:
The Cambridge Handbook of Physics F
- Page 12:
Contents Preface page vii How to us
- Page 16:
Preface In A Brief History of Time,
- Page 20:
How to use this book The format is
- Page 26:
4 Units, constants, and conversions
- Page 30:
6 Units, constants, and conversions
- Page 34:
8 Units, constants, and conversions
- Page 38:
10 Units, constants, and conversion
- Page 42:
12 Units, constants, and conversion
- Page 46:
14 Units, constants, and conversion
- Page 50:
16 Units, constants, and conversion
- Page 54:
18 Units, constants, and conversion
- Page 58:
20 Mathematics 2.2 Vectors and matr
- Page 62:
22 Mathematics Divergence Rectangul
- Page 66:
24 Mathematics Matrix algebra a ⎛
- Page 70:
26 Mathematics Commutators Commutat
- Page 74:
28 Mathematics Power series Binomia
- Page 78:
30 Mathematics Inequalities Triangl
- Page 82:
32 Mathematics 2.5 Trigonometric an
- Page 86:
34 Mathematics Trigonometric and hy
- Page 90:
36 Mathematics Plane triangles Sine
- Page 94:
38 Mathematics Conic sections y y y
- Page 98:
40 Mathematics 2.7 Differentiation
- Page 102:
42 Mathematics Partial derivatives
- Page 106:
44 Mathematics 2.8 Integration Stan
- Page 110:
46 Mathematics Definite integrals
- Page 114:
48 Mathematics Associated Legendre
- Page 118:
50 Mathematics Delta functions Kron
- Page 122:
52 Mathematics 2.11 Fourier series
- Page 126:
54 Mathematics Fourier transform pa
- Page 130:
56 Mathematics Laplace transform pa
- Page 134:
58 Mathematics Continuous probabili
- Page 138:
60 Mathematics 2.14 Numerical metho
- Page 142:
62 Mathematics Numerical solutions
- Page 146:
64 Dynamics and mechanics 3.2 Frame
- Page 150: 66 Dynamics and mechanics Rotating
- Page 154: 68 Dynamics and mechanics 3.4 Parti
- Page 158: 70 Dynamics and mechanics Rocketry
- Page 162: 72 Dynamics and mechanics Rutherfor
- Page 166: 74 Dynamics and mechanics 3.5 Rigid
- Page 170: 76 Dynamics and mechanics Centres o
- Page 174: 78 Dynamics and mechanics 3.6 Oscil
- Page 178: 80 Dynamics and mechanics 3.8 Elast
- Page 182: 82 Dynamics and mechanics Bending b
- Page 186: 84 Dynamics and mechanics 3.9 Fluid
- Page 190: 86 Dynamics and mechanics Character
- Page 194: 88 Dynamics and mechanics Surface t
- Page 198: 90 Quantum physics 4.2 Quantum defi
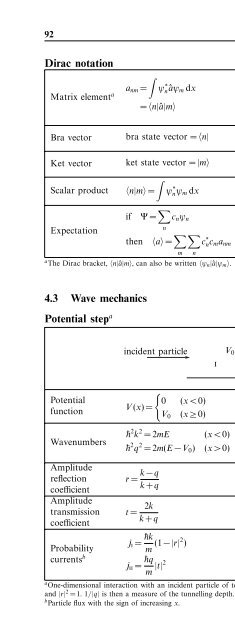
- Page 204: 4.3 Wave mechanics 93 Potential wel
- Page 208: 4.4 Hydrogenic atoms 95 Harmonic os
- Page 212: 4.4 Hydrogenic atoms 97 Orbital ang
- Page 216: 4.5 Angular momentum 99 Clebsch-Gor
- Page 220: 4.5 Angular momentum 101 Quantum pa
- Page 224: 4.7 High energy and nuclear physics
- Page 228: Chapter 5 Thermodynamics 5.1 Introd
- Page 232: 5.2 Classical thermodynamics 107 Cy
- Page 236: 5.2 Classical thermodynamics 109 Ma
- Page 240: 5.3 Gas laws 111 Van der Waals gas
- Page 244: 5.4 Kinetic theory 113 Transport pr
- Page 248: 5.5 Statistical thermodynamics 115
- Page 252:
5.6 Fluctuations and noise 117 Nois
- Page 256:
5.7 Radiation processes 119 Photome
- Page 260:
5.7 Radiation processes 121 Blackbo
- Page 266:
124 Solid state physics 6.2 Periodi
- Page 270:
126 Solid state physics 6.3 Crystal
- Page 274:
128 Solid state physics Dislocation
- Page 278:
130 Solid state physics Debye theor
- Page 282:
132 Solid state physics 6.5 Electro
- Page 286:
134 Solid state physics Band theory
- Page 290:
136 Electromagnetism 7.2 Static fie
- Page 294:
138 Electromagnetism Electric field
- Page 298:
140 Electromagnetism Maxwell’s eq
- Page 302:
142 Electromagnetism 7.4 Fields ass
- Page 306:
144 Electromagnetism Paramagnetism
- Page 310:
146 Electromagnetism Electromagneti
- Page 314:
148 Electromagnetism Resonant LCR c
- Page 318:
150 Electromagnetism 7.7 Transmissi
- Page 322:
152 Electromagnetism 7.8 Waves in a
- Page 326:
154 Electromagnetism Reflection, re
- Page 330:
156 Electromagnetism Cherenkov radi
- Page 334:
158 Electromagnetism Magnetohydrody
- Page 338:
160 Electromagnetism Bremsstrahlung
- Page 342:
162 Optics 8.2 Interference Newton
- Page 346:
164 Optics 8.3 Fraunhofer diffracti
- Page 350:
166 Optics 8.4 Fresnel diffraction
- Page 354:
168 Optics 8.5 Geometrical optics L
- Page 358:
170 Optics 8.6 Polarisation Ellipti
- Page 362:
172 Optics 8.7 Coherence (scalar th
- Page 366:
174 Optics Lasers a R 1 R 2 r 1 r 2
- Page 370:
176 Astrophysics 9.2 Solar system d
- Page 374:
178 Astrophysics Ecliptic coordinat
- Page 378:
180 Astrophysics Planetary bodies B
- Page 382:
182 Astrophysics Stellar fusion pro
- Page 386:
184 Astrophysics 9.6 Cosmology Cosm
- Page 392:
Index Section headings are shown in
- Page 396:
Index 189 and Johnson noise [5.141]
- Page 400:
Index 191 to mass ratio of electron
- Page 404:
Index 193 Coulomb logarithm [7.254]
- Page 408:
Index 195 rectangular aperture [8.3
- Page 412:
Index 197 fields, 139 wave speed [7
- Page 416:
Index 199 energy [6.73], 133 temper
- Page 420:
Index 201 temperature scale [5.1],
- Page 424:
Index 203 Schrödinger equation [4.
- Page 428:
Index 205 Lagrange’s identity [2.
- Page 432:
Index 207 wire [7.34], 138 wire loo
- Page 436:
Index 209 Numerical methods, 60 Num
- Page 440:
Index 211 energy in Lagrangian [3.2
- Page 444:
Index 213 transmission line [7.179]
- Page 448:
Index 215 solenoid finite [7.38], 1
- Page 452:
Index 217 diffusion equation [2.340
- Page 456:
Index 219 84 vorticity and potentia