You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
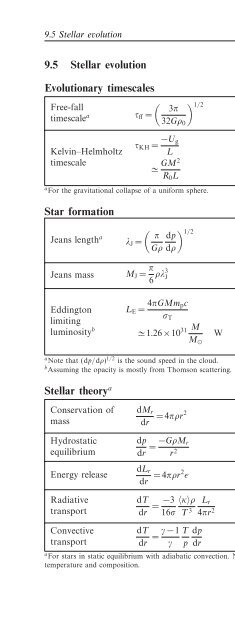
9.5 Stellar evolution<br />
181<br />
9.5 Stellar evolution<br />
Evolutionary timescales<br />
( )<br />
Free-fall<br />
1/2 3π<br />
timescale a τ ff =<br />
(9.53)<br />
32Gρ 0<br />
Kelvin–Helmholtz<br />
timescale<br />
τ KH = −U g<br />
L<br />
≃ GM2<br />
R 0 L<br />
a For the gravitational collapse <strong>of</strong> a uniform sphere.<br />
(9.54)<br />
(9.55)<br />
τ ff<br />
G<br />
ρ 0<br />
τ KH<br />
U g<br />
M<br />
R 0<br />
L<br />
free-fall timescale<br />
constant <strong>of</strong> gravitation<br />
initial mass density<br />
Kelvin–Helmholtz timescale<br />
gravitational potential energy<br />
body’s mass<br />
body’s initial radius<br />
body’s luminosity<br />
Star formation<br />
( ) 1/2<br />
Jeans length a π dp<br />
λ J =<br />
(9.56)<br />
Gρ dρ<br />
λ J<br />
G<br />
ρ<br />
p<br />
Jeans length<br />
constant <strong>of</strong> gravitation<br />
cloud mass density<br />
pressure<br />
Jeans mass M J = π 6 ρλ3 J (9.57) M J (spherical) Jeans mass<br />
Eddington<br />
limiting<br />
luminosity b<br />
L E = 4πGMm pc<br />
σ T<br />
(9.58)<br />
≃ 1.26×10 31 M M ⊙<br />
W (9.59)<br />
a Note that (dp/dρ) 1/2 is the sound speed in the cloud.<br />
b Assuming the opacity is mostly from Thomson scattering.<br />
L E<br />
M<br />
M ⊙<br />
m p<br />
c<br />
σ T<br />
Eddington luminosity<br />
stellar mass<br />
solar mass<br />
proton mass<br />
speed <strong>of</strong> light<br />
Thomson cross section<br />
Stellar theory a<br />
Conservation <strong>of</strong><br />
mass<br />
Hydrostatic<br />
equilibrium<br />
dM r<br />
dr =4πρr2 (9.60)<br />
dp<br />
dr = −GρM r<br />
r 2 (9.61)<br />
r<br />
M r<br />
ρ<br />
p<br />
G<br />
radial distance<br />
mass interior to r<br />
mass density<br />
pressure<br />
constant <strong>of</strong> gravitation<br />
Energy release<br />
dL r<br />
dr =4πρr2 ɛ (9.62)<br />
L r<br />
ɛ<br />
luminosity interior to r<br />
power generated per unit mass<br />
Radiative<br />
dT<br />
transport<br />
dr = −3<br />
T temperature<br />
〈κ〉ρ L r<br />
16σ T 3 4πr 2 (9.63) σ Stefan–Boltzmann constant<br />
〈κ〉 mean opacity<br />
Convective dT<br />
transport<br />
dr = γ −1 T dp<br />
(9.64) γ ratio <strong>of</strong> heat capacities, c p /c V<br />
γ p dr<br />
a For stars in static equilibrium with adiabatic convection. Note that ρ is a function <strong>of</strong> r. κ and ɛ are functions <strong>of</strong><br />
temperature and composition.<br />
9