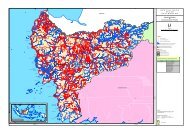
Decentralization of Forest Administration in Indonesia, Implications ...
Decentralization of Forest Administration in Indonesia, Implications ...
Decentralization of Forest Administration in Indonesia, Implications ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
30<br />
<strong>Forest</strong> <strong>Adm<strong>in</strong>istration</strong> and <strong>Forest</strong>ry Sector Development Prior to 1998<br />
Development Plann<strong>in</strong>g, First Phase 1961-1969 (Ketetapan MPRS No. II/MPRS/1960 ttg<br />
Garis-garis Besar Rencana Pembangunan Nasional Semesta Berencana Tahap Pertama<br />
1961-1969).<br />
8<br />
See Magenda (1991) for details on how this struggle played out between Jakarta and the<br />
prov<strong>in</strong>cial apparatus <strong>in</strong> East Kalimantan.<br />
9<br />
The procedures for conduct<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>ventory, survey, boundary determ<strong>in</strong>ation and mark<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
and subsequent classification <strong>of</strong> the <strong>Forest</strong> Estate were detailed <strong>in</strong> Government Regulation<br />
33/1970. Systematic classification <strong>of</strong> the nation’s <strong>Forest</strong> Areas was not implemented, however,<br />
for over a decade. Barber (1990:12) notes that “systematic national implementation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
Basic <strong>Forest</strong>ry Law’s classification and plann<strong>in</strong>g mandate only began <strong>in</strong> 1980, when the<br />
M<strong>in</strong>ister <strong>of</strong> <strong>Forest</strong>ry [sic] sent a memorandum to the Governors <strong>of</strong> all Prov<strong>in</strong>ces, <strong>in</strong>form<strong>in</strong>g<br />
them that the Department would prepare a ‘Consensus <strong>Forest</strong> Land Use Plan’ (Tata Guna<br />
Hutan Kesepakatan, TGHK) for each prov<strong>in</strong>ce, <strong>in</strong> cooperation with all agencies <strong>in</strong>volved<br />
with land use at the prov<strong>in</strong>cial level.”<br />
10<br />
In formulat<strong>in</strong>g these requirements, forestry policymakers assumed that logged-over forest<br />
would naturally regenerate at an average rate <strong>of</strong> 1-2 m 3 per ha per year, and as such would<br />
be able to susta<strong>in</strong> a selective harvest on average every 35 years. To promote concessionaire<br />
compliance with the HPH contract, the <strong>Forest</strong>ry Department required that private timber<br />
operators submit for approval 20-year, 5-year, and annual work plans. Approval <strong>of</strong> the yearly<br />
work plan was supposed to <strong>in</strong>volve cruis<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the applicant’s logg<strong>in</strong>g block by prov<strong>in</strong>cial<br />
forestry <strong>of</strong>ficials <strong>in</strong> order to determ<strong>in</strong>e the company’s annual allowable cut (AAC).<br />
11<br />
At the national level, <strong>Indonesia</strong>’s forest resources were adm<strong>in</strong>istered by the Directorate<br />
General <strong>of</strong> <strong>Forest</strong>ry <strong>in</strong> the M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong> Agriculture until 1983, at which po<strong>in</strong>t the M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>Forest</strong>ry was given cab<strong>in</strong>et status.<br />
12<br />
FOB refers to ‘freight on board’, or the price <strong>of</strong> goods sold with transport costs excluded.<br />
13<br />
‘Cutt<strong>in</strong>g dur<strong>in</strong>g the flood’, a term to describe the nonmechanized logg<strong>in</strong>g technique. The<br />
operators cut logs by hand and floated them out <strong>of</strong> the forest on swollen rivers dur<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
monsoon season, us<strong>in</strong>g no roads, trucks, or bulldozers (Ross 2001).<br />
14<br />
Much more recently, the same argument has been made by MoF <strong>of</strong>ficials seek<strong>in</strong>g to halt<br />
the allocation <strong>of</strong> small-scale logg<strong>in</strong>g and forest conversion permits issued by district<br />
governments under <strong>Indonesia</strong>’s post-1999 decentralization process.<br />
15<br />
In East Kalimantan, for <strong>in</strong>stance, Banjarese <strong>of</strong>ficials who had controlled the prov<strong>in</strong>ce and<br />
kabupaten-level bureaucracies through the first years <strong>of</strong> the New Order period, lost their<br />
ma<strong>in</strong> source <strong>of</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ance for both bus<strong>in</strong>ess ventures and political endeavors (Magenda 1991).<br />
They were replaced <strong>in</strong> many key positions by members <strong>of</strong> the Regional Military Command<br />
(Komando Daerah Militer, Kodam) for East Kalimantan, which was dom<strong>in</strong>ated by Javanese<br />
<strong>of</strong>ficers connected to the M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong> Defense <strong>in</strong> Jakarta through both the formal cha<strong>in</strong> <strong>of</strong><br />
command and <strong>in</strong>formal patronage networks.