Here - American Geriatrics Society
Here - American Geriatrics Society
Here - American Geriatrics Society
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
P OSTER<br />
A BSTRACTS<br />
B47<br />
The Impact of Cognitive Impairment on Mortality in Older Adults<br />
with Heart Failure.<br />
T. Gure, 1 C. Blaum, 1,3 J. Ha, 1 S. Hummel, 4 L. Min, 1,3 C. Cigolle, 6,3<br />
A. Galecki, 1 K. Langa. 2,5 1. Geriatric & Palliative Medicine, University<br />
of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI; 2. General Internal Medicine, University<br />
of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI; 3. GRECC, VA Healthcare System, Ann<br />
Arbor, MI; 4. Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann<br />
Arbor, MI; 5. VA Center for Practice Management & Outcomes<br />
Research, VA Healthcare System, Ann Arbor, MI; 6. Family Medicine,<br />
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI.<br />
Supported By: The National Institute on Aging (NIA) provides<br />
funding for the Health and Retirement Study (U01 AG09740)<br />
which is performed at the Institute for Social Research, University<br />
of Michigan; NIA grants R01 AG027010 and R01 AG030155<br />
(Langa); Ann Arbor VA Geriatric Research, Clinical and Education<br />
Center (Blaum, Cigolle, and Min); NHLBI grant K23 HL109176<br />
(Hummel); AHRQ grants R21 HS017621 and R21 HS 019459<br />
(Min); NIA grant K08 AG031837 (Cigolle); NIA Diversity<br />
Supplement award R01 AG027010-02S1 (Gure); John A. Hartford<br />
Foundation Center of Excellence (Cigolle, Gure, and Min); the NIA<br />
Claude D. Pepper Center Research Career Development Core<br />
(Cigolle, Gure, and Min); National Center for Research Resources<br />
UL1 RR024986 (Gure).<br />
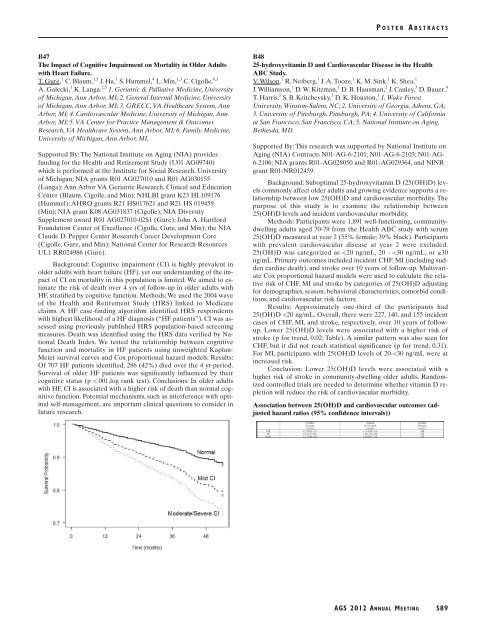
Background: Cognitive impairment (CI) is highly prevalent in<br />
older adults with heart failure (HF), yet our understanding of the impact<br />
of CI on mortality in this population is limited. We aimed to estimate<br />
the risk of death over 4 yrs of follow-up in older adults with<br />
HF, stratified by cognitive function. Methods: We used the 2004 wave<br />
of the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) linked to Medicare<br />
claims. A HF case-finding algorithm identified HRS respondents<br />
with highest likelihood of a HF diagnosis (“HF patients”). CI was assessed<br />
using previously published HRS population-based screening<br />
measures. Death was identified using the HRS data verified by National<br />
Death Index. We tested the relationship between cognitive<br />
function and mortality in HF patients using unweighted Kaplan-<br />
Meier survival curves and Cox proportional hazard models. Results:<br />
Of 707 HF patients identified, 286 (42%) died over the 4 yr-period.<br />
Survival of older HF patients was significantly influenced by their<br />
cognitive status (p