programma & abstracts - Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie
programma & abstracts - Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie
programma & abstracts - Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MSK/Thorax/Diversen 10<br />
O10.2<br />
CT-ARTHROGRAPHY TO MEASURE<br />
CARTILAGE QUALITY: INFLUENCE OF<br />
SULPHATED GLYCOSAMINOGLYCAN<br />
CONTENT AND STRUCTURAL<br />
COMPOSITION OF EXTRACELLULAR<br />
MATRIX ON CONTRAST AGENT DIFFUSION<br />
INTO CARTILAGE<br />
J. van Tiel, M. Siebelt, J.H. Waarsing, M. van Straten,<br />
G.P. Krestin, H. Weinans, E.H.G. Oei<br />
Erasmus Medisch Centrum, Rotterdam<br />
Purpose: To assess the potential of CT-arthrography to<br />
evaluate cartilage quality in terms of sulphated glycosaminoglycan<br />
content (sGAG) and structural composition of the<br />
extra-cellular matrix (ECM).<br />
Methods: Eleven human cadaveric knee joints were<br />
scanned on a second generation dual source spiral CT scanner<br />
before and after intra-articular injection of a negatively<br />
charged contrast agent. Mean X-ray attenuation values of<br />
both scans were calculated in seven regions of interest<br />
(ROIs) of the cartilage (weight-bearing condyles and plateaus,<br />
non weight-bearing condyles and patella). Next, all<br />
ROIs were rescanned with contrast-enhanced<br />
micro-CT (μCT), which served as reference standard because<br />
it accurately measures sGAG content and hence quality<br />
of cartilage. Correlation between mean X-ray attenuation<br />
values of CT-arthrography and μCT was analyzed with linear<br />
regression. Additionally, residual values from the linear fit<br />
between unenhanced CT and μCT were used as a covariate<br />
measure to identify the influence of structural composition<br />
of cartilage ECM, i.e. without influence of sGAG, on contrast<br />
diffusion into cartilage.<br />
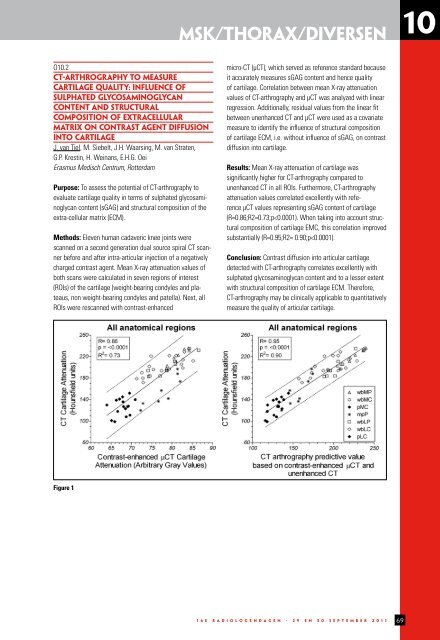
Results: Mean X-ray attenuation of cartilage was<br />
significantly higher for CT-arthrography compared to<br />
unenhanced CT in all ROIs. Furthermore, CT-arthrography<br />
attenuation values correlated excellently with reference<br />
μCT values representing sGAG content of cartilage<br />
(R=0.86;R2=0.73;p