programma & abstracts - Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie
programma & abstracts - Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie
programma & abstracts - Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
posterpresentaties<br />
P<br />
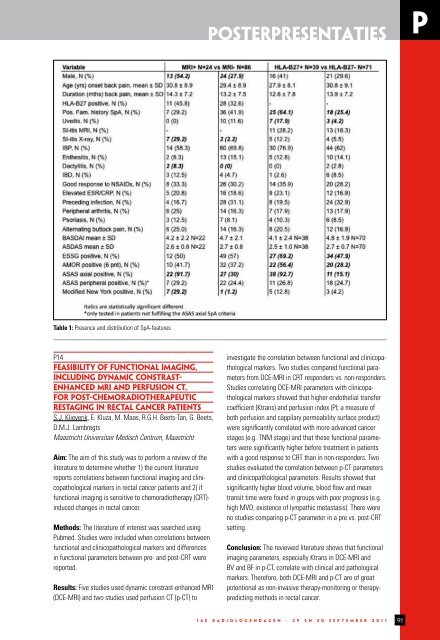
Table 1: Presence and distribution of SpA-features.<br />
P14<br />
FEASIBILITY OF FUNCTIONAL IMAGING,<br />
INCLUDING DYNAMIC CONSTRAST-<br />
ENHANCED MRI AND PERFUSION CT,<br />
FOR POST-CHEMORADIOTHERAPEUTIC<br />
RESTAGING IN RECTAL CANCER PATIENTS<br />
S.J. Klieverik, E. Kluza, M. Maas, R.G.H. Beets-Tan, G. Beets,<br />
D.M.J. Lambregts<br />
Maastricht Universitair Medisch Centrum, Maastricht<br />
Aim: The aim of this study was to perform a review of the<br />
literature to determine whether 1) the current literature<br />
reports correlations between functional imaging and clinicopathological<br />
markers in rectal cancer patients and 2) if<br />
functional imaging is sensitive to chemoradiotherapy (CRT)-<br />
induced changes in rectal cancer.<br />
Methods: The literature of interest was searched using<br />
Pubmed. Studies were included when correlations between<br />
functional and clinicopathological markers and differences<br />
in functional parameters between pre- and post-CRT were<br />
reported.<br />
Results: Five studies used dynamic constrast-enhanced MRI<br />
(DCE-MRI) and two studies used perfusion CT (p-CT) to<br />
investigate the correlation between functional and clinicopathological<br />
markers. Two studies compared functional parameters<br />
from DCE-MRI in CRT responders vs. non-responders.<br />
Studies correlating DCE-MRI parameters with clinicopathological<br />
markers showed that higher endothelial transfer<br />
coefficient (Ktrans) and perfusion index (PI; a measure of<br />
both perfusion and cappilary permeability surface product)<br />
were significantly correlated with more advanced cancer<br />
stages (e.g. TNM stage) and that these functional parameters<br />
were significantly higher before treatment in patients<br />
with a good response to CRT than in non-responders. Two<br />
studies evaluated the correlation between p-CT parameters<br />
and clinicopathological parameters. Results showed that<br />
significantly higher blood volume, blood flow and mean<br />
transit time were found in groups with poor prognosis (e.g.<br />
high MVD, existence of lympathic metastasis). There were<br />
no studies comparing p-CT parameter in a pre vs. post-CRT<br />
setting.<br />
Conclusion: The reviewed literature shows that functional<br />
imaging parameters, especially Ktrans in DCE-MRI and<br />
BV and BF in p-CT, correlate with clinical and pathological<br />
markers. Therefore, both DCE-MRI and p-CT are of great<br />
potentional as non-invasive therapy-monitoring or therapypredicting<br />
methods in rectal cancer.<br />
1 6 E R A D I O L O G E N D A G E N - 2 9 e n 3 0 S E P T E M B E R 2 0 1 1<br />
91