Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
39057_ch14_<strong>cell</strong>bio.qxd 8/28/06 5:11 PM Page 609<br />
Calcium binding causes a conformational change in calmodulin<br />
Calcium-free<br />
calmodulin<br />
calmodulin free + 4 Ca 2+<br />
Calcium-bound<br />
calmodulin bound to<br />
target peptide <strong>of</strong> CaMK<br />
Ca 2+<br />
target<br />
(Ca 2+ ) 4<br />
. calmodulin . active target<br />
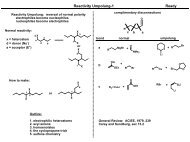
FIGURE 14.16 Ribbon diagrams representing<br />
the crystal structures <strong>of</strong> calmodulin free<br />
<strong>of</strong> Ca2+ and bound to four Ca2+ ions reveal<br />
the huge conformational change that<br />
calmodulin undergoes upon Ca2+ binding.<br />
Ca2+-calmodulin causes activity changes in<br />
target proteins. The bottom panel shows<br />
the activation <strong>of</strong> a target by calmodulin as<br />
a function <strong>of</strong> the intra<strong>cell</strong>ular free Ca2+ concentration.<br />
The requirement for binding<br />
four Ca2+ ions to induce the conformational<br />
transition results in cooperative activation<br />
<strong>of</strong> targets. Activity increases from 10% to<br />
90% as the Ca2+ concentration increases<br />
only 10-fold. Structures generated from<br />
Protein Data Bank files 1CFD and 1MXE.<br />
Activation <strong>of</strong> target<br />
by calmodulin (%)<br />
100<br />
90%<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
10%<br />
3 x 10 -8 3 x 10 -7 3 x 10 -6<br />
[Ca 2+ ]<br />
brane Ca2+ channels activate intra<strong>cell</strong>ular functions).<br />
In addition to the proteins that are regulated<br />
by binding Ca2+ directly, many other proteins respond<br />
to Ca2+ by binding a widespread Ca2+ sensor,<br />
the small, ~17 kDa protein calmodulin.<br />
Calmodulin requires the binding <strong>of</strong> four molecules<br />
<strong>of</strong> Ca2+ to become fully active, and binding<br />
is highly cooperative, generating a sigmoid<br />
activation pr<strong>of</strong>ile illustrated in FIGURE 14.16.<br />
Calmodulin generally binds its targets in a Ca2+dependent<br />
manner, but Ca2+-free calmodulin<br />
may remain bound but inactive in some cases.<br />
For example, calmodulin is a constitutive subunit<br />
<strong>of</strong> phosphorylase kinase that is activated<br />
upon Ca2+ binding. Higher plants again make<br />
major modifications to this paradigm. Calmodulin<br />
is not expressed as a distinct protein but, instead,<br />
is found as a domain in Ca2+-regulated proteins.<br />
In yet another variation, the adenylyl cyclase secreted<br />
by the pathogenic bacterium Bordetella pertussis<br />
is inactive outside <strong>cell</strong>s but is activated by<br />
Ca2+-free calmodulin in animal <strong>cell</strong>s, where its<br />
rapid production <strong>of</strong> cAMP is highly toxic.<br />
14.16<br />
Lipids and lipid-derived<br />
compounds are <strong>signaling</strong><br />
molecules<br />
Key concepts<br />
• Multiple lipid-derived second messengers are<br />
produced in membranes.<br />
• Phospholipase Cs release soluble and lipid second<br />
messengers in response to diverse inputs.<br />
• Channels and transporters are modulated by<br />
different lipids in addition to inputs from other<br />
sources.<br />
• PI 3-kinase synthesizes PIP 3<br />
to modulate <strong>cell</strong><br />
shape and motility.<br />
• PLD and PLA 2<br />
create other lipid second<br />
messengers.<br />
Signals that originate at the plasma membrane<br />
may have soluble regulatory targets in the cytoplasm<br />
or intra<strong>cell</strong>ular organelles, but integral<br />
plasma membrane proteins are also subject to<br />
acute controls. For these targets, lipid second<br />
messengers may be primary inputs. Lipids derived<br />
from membrane phospholipids or other<br />
14.16 Lipids and lipid-derived compounds are <strong>signaling</strong> molecules 609