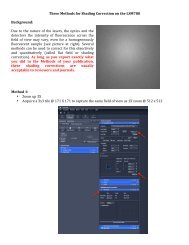
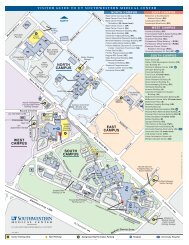
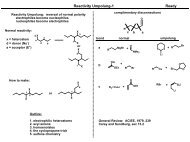
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
39057_ch14_<strong>cell</strong>bio.qxd 8/28/06 5:11 PM Page 640<br />
Review<br />
Mangelsdorf, D. J. et al., 1995. The nuclear<br />
receptor superfamily: the second decade.<br />
Cell v. 83 p. 835–839.<br />
Smith, C. L. and O’Malley, B. W., 2004.<br />
Coregulator function: a key to understanding<br />
tissue specificity <strong>of</strong> selective receptor<br />
modulators. Endocr. Rev. v. 25 p.<br />
45–71.<br />
Research<br />
Brzozowski A. M., Pike, A. C., Dauter, Z.,<br />
Hubbard, R. E., Bonn, T., Engstrom, O.,<br />
Ohman, L., Green, G. L., Gustafsson, J. A.,<br />
and Carlquist, M., 1997. Molecular basis<br />
<strong>of</strong> agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen<br />
receptor. Nature v. 389 p. 753–758.<br />
14.20 G protein <strong>signaling</strong> modules are widely<br />
used and highly adaptable<br />
Review<br />
Clapham, D. E. and Neer, E. J., 1997. G protein<br />
subunits. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol.<br />
Toxicol. v. 37 p. 167–203.<br />
Filipek, S., Teller, D. C., Palczewski, K., and<br />
Stenkamp, R., 2003. The crystallographic<br />
model <strong>of</strong> rhodopsin and its use in studies<br />
<strong>of</strong> other G protein-coupled receptors.<br />
Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. v. 32 p.<br />
375–397.<br />
Ross, E. M. and Wilkie, T. M., 2000. GTPaseactivating<br />
proteins for heterotrimeric G<br />
proteins: Regulators <strong>of</strong> G protein <strong>signaling</strong><br />
(RGS) and RGS-like proteins. Annu.<br />
Rev. Biochem. v. 69 p. 795–827.<br />
Ross, E. M., 1989. Signal sorting and amplification<br />
through G protein-coupled receptors.<br />
Neuron v. 3 p. 141–152.<br />
Sprang, S. R., 1997. G proteins, effectors and<br />
GAPs: structure and mechanism. Curr.<br />
Opin. Struct. Biol. v. 7 p. 849–856.<br />
Sprang, S. R., 1997. G protein mechanisms:<br />
Insights from structural analysis. Annu.<br />
Rev. Biochem. v. 66 p. 639–678.<br />
Research<br />
Benke, T., Motoshima, C. A., Fox, H., Le<br />
Trong, B. A., Teller, I., Okada, D. C.,<br />
Stenkamp, T., Yamamoto, R. E., and<br />
Miyano, M., 2000. Crystal structure <strong>of</strong><br />
rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor.<br />
Science v. 289 p. 739–745.<br />
Chen, C. -K., Burns, M. E., He, W., Wensel, T.<br />
G., Baylor, D. A., and Simon, M. I., 2000.<br />
Slowed recovery <strong>of</strong> rod photoresponse in<br />
mice lacking the GTPase acceleration protein<br />
RGS9-1. Nature, v. 403 p. 557–560.<br />
Palczewski, K., Kumasaka, T., Hori, T.,<br />
Behnke , C. A., Motoshima, H., Fox, B.<br />
A., Le Trong, I., Teller, D. C., Okada, T.,<br />
Stenkamp, R. E., Yamamoto, M., and<br />
Miyano, M., 2000. Crystal structure <strong>of</strong><br />
rhodopsin: a G protein-coupled receptor.<br />
Science v. 289 p. 739–745.<br />
Wall, M. A., Coleman, D. E., Lee, E., Iniguez-<br />
Lluhi, J. A., Posner, B. A., Gilman, A. G.,<br />
and Sprang, S. R., 1995. The structure <strong>of</strong><br />
the G protein heterotrimer G i1<br />
1<br />
2<br />
. Cell<br />
v. 83 p. 1047–1058.<br />
14.23 Small, monomeric GTP-binding proteins<br />
are multiuse switches<br />
Review<br />
Bishop, A. L. and Hall, A., 2000. Rho GTPases<br />
and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. v.<br />
348 pt. 2 p. 241–255.<br />
Kuersten, S., Ohno, M., and Mattaj, I. W.,<br />
2001. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: Ran,<br />
beta and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. v. 11 p.<br />
497–503.<br />
Takai, Y., Sasaki, T., and Matozaki, T., 2001.<br />
Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol. Rev.<br />
v. 81 p. 153–208.<br />
14.24 Protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation<br />
is a major regulatory mechanism in<br />
the <strong>cell</strong><br />
Review<br />
Cohen, S., 1983. The epidermal growth factor<br />
(EGF). Cancer v. 51 p. 1787–1791.<br />
Fischer, E. H., 1997. “Protein phosphorylation<br />
and <strong>cell</strong>ular regulation, II,” in Nobel<br />
Lectures, Physiology or Medicine 1991–1995,<br />
N., Ringertz, Ed., Singapore: World<br />
Scientific Publishing Co.<br />
Krebs, G., 1993. Protein phosphorylation and<br />
<strong>cell</strong>ular regulation. Bioscience Reports v. 13<br />
p. 127–142.<br />
Manning, G., Whyte, D. B., Martinez, R.,<br />
Hunter, T., and Sudarsanam, S., 2002.<br />
The protein kinase complement <strong>of</strong> the<br />
human genome. Science v. 298 p.<br />
1912–1934.<br />
Newton, A. C., 2003. Regulation <strong>of</strong> the ABC<br />
kinases by phosphorylation: protein kinase<br />
C as a paradigm. Biochem. J. v. 370 p.<br />
361–371.<br />
Nolen, B., Taylor, S., and Ghosh, G., 2004.<br />
Regulation <strong>of</strong> protein kinases; controlling<br />
activity through activation segment conformation.<br />
Mol. Cell v. 15 p. 661–675.<br />
Turk, B. E. and Cantley, L. C., 2003. Peptide<br />
libraries: at the crossroads <strong>of</strong> proteomics<br />
and bioinformatics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol.<br />
v. 7 p. 84–90.<br />
Research<br />
Canagarajah, B. J., Khokhlatchev, A., Cobb,<br />
M. H., and Goldsmith, E. J., 1997.<br />
Activation mechanism <strong>of</strong> the MAP kinase<br />
ERK2 by dual phosphorylation. Cell v. 90<br />
p. 859–869.<br />
Ginty, D. D., Kornhauser, J. M., Thompson,<br />
640 CHAPTER 14 <strong>Principles</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>cell</strong> <strong>signaling</strong>