Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
Principles of cell signaling - UT Southwestern
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
39057_ch14_<strong>cell</strong>bio.qxd 8/28/06 5:11 PM Page 635<br />
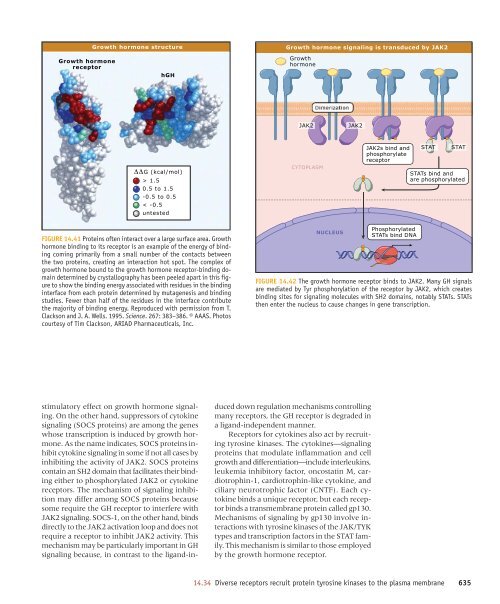
Growth hormone structure<br />
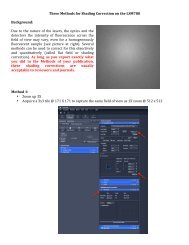
Growth hormone <strong>signaling</strong> is transduced by JAK2<br />
Growth hormone<br />
receptor<br />
hGH<br />
Growth<br />
hormone<br />
Dimerization<br />
JAK2<br />
JAK2<br />
ΔΔG (kcal/mol)<br />
> 1.5<br />
0.5 to 1.5<br />
-0.5 to 0.5<br />
< -0.5<br />
untested<br />
CYTOPLASM<br />
JAK2s bind and<br />
phosphorylate<br />
receptor<br />
STAT<br />
STAT<br />
STATs bind and<br />
are phosphorylated<br />
FIGURE 14.41 Proteins <strong>of</strong>ten interact over a large surface area. Growth<br />
hormone binding to its receptor is an example <strong>of</strong> the energy <strong>of</strong> binding<br />
coming primarily from a small number <strong>of</strong> the contacts between<br />
the two proteins, creating an interaction hot spot. The complex <strong>of</strong><br />
growth hormone bound to the growth hormone receptor-binding domain<br />
determined by crystallography has been peeled apart in this figure<br />
to show the binding energy associated with residues in the binding<br />
interface from each protein determined by mutagenesis and binding<br />
studies. Fewer than half <strong>of</strong> the residues in the interface contribute<br />
the majority <strong>of</strong> binding energy. Reproduced with permission from T.<br />
Clackson and J. A. Wells. 1995. Science. 267: 383–386. © AAAS. Photos<br />
courtesy <strong>of</strong> Tim Clackson, ARIAD Pharmaceuticals, Inc.<br />
NUCLEUS<br />
Phosphorylated<br />
STATs bind DNA<br />
FIGURE 14.42 The growth hormone receptor binds to JAK2. Many GH signals<br />
are mediated by Tyr phosphorylation <strong>of</strong> the receptor by JAK2, which creates<br />
binding sites for <strong>signaling</strong> molecules with SH2 domains, notably STATs. STATs<br />
then enter the nucleus to cause changes in gene transcription.<br />
stimulatory effect on growth hormone <strong>signaling</strong>.<br />
On the other hand, suppressors <strong>of</strong> cytokine<br />
<strong>signaling</strong> (SOCS proteins) are among the genes<br />
whose transcription is induced by growth hormone.<br />
As the name indicates, SOCS proteins inhibit<br />
cytokine <strong>signaling</strong> in some if not all cases by<br />
inhibiting the activity <strong>of</strong> JAK2. SOCS proteins<br />
contain an SH2 domain that facilitates their binding<br />
either to phosphorylated JAK2 or cytokine<br />
receptors. The mechanism <strong>of</strong> <strong>signaling</strong> inhibition<br />
may differ among SOCS proteins because<br />
some require the GH receptor to interfere with<br />
JAK2 <strong>signaling</strong>. SOCS-1, on the other hand, binds<br />
directly to the JAK2 activation loop and does not<br />
require a receptor to inhibit JAK2 activity. This<br />
mechanism may be particularly important in GH<br />
<strong>signaling</strong> because, in contrast to the ligand-induced<br />
down regulation mechanisms controlling<br />
many receptors, the GH receptor is degraded in<br />
a ligand-independent manner.<br />
Receptors for cytokines also act by recruiting<br />
tyrosine kinases. The cytokines—<strong>signaling</strong><br />
proteins that modulate inflammation and <strong>cell</strong><br />
growth and differentiation—include interleukins,<br />
leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin M, cardiotrophin-1,<br />
cardiotrophin-like cytokine, and<br />
ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF). Each cytokine<br />
binds a unique receptor, but each receptor<br />
binds a transmembrane protein called gp130.<br />
Mechanisms <strong>of</strong> <strong>signaling</strong> by gp130 involve interactions<br />
with tyrosine kinases <strong>of</strong> the JAK/TYK<br />
types and transcription factors in the STAT family.<br />
This mechanism is similar to those employed<br />
by the growth hormone receptor.<br />
14.34 Diverse receptors recruit protein tyrosine kinases to the plasma membrane 635