WP6-Brochure-E4 brochure - ELA European Lift Association.
WP6-Brochure-E4 brochure - ELA European Lift Association.
WP6-Brochure-E4 brochure - ELA European Lift Association.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
• Hall Call allocation and Double‐Deck lifts<br />
The use of hall call allocation enables the system to assign the number of passengers that is<br />
more likely to match the counterbalancing ratio of the lift, thus minimising the energy used.<br />
This is especially pertinent in low traffic periods, when it is less important that lifts travel at<br />
their maximum capacity.<br />
One solution to improve the traffic handling capabilities of a lift system in very high‐rise<br />
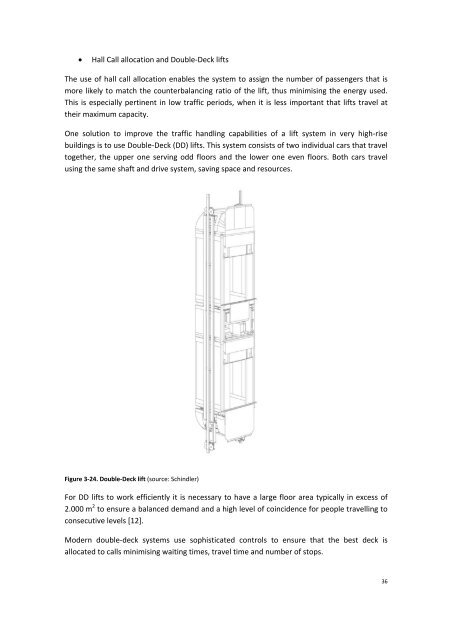
buildings is to use Double‐Deck (DD) lifts. This system consists of two individual cars that travel<br />
together, the upper one serving odd floors and the lower one even floors. Both cars travel<br />
using the same shaft and drive system, saving space and resources.<br />
Figure 3‐24. Double‐Deck lift (source: Schindler)<br />
For DD lifts to work efficiently it is necessary to have a large floor area typically in excess of<br />
2.000 m 2 to ensure a balanced demand and a high level of coincidence for people travelling to<br />
consecutive levels [12].<br />
Modern double‐deck systems use sophisticated controls to ensure that the best deck is<br />
allocated to calls minimising waiting times, travel time and number of stops.<br />
36