WP6-Brochure-E4 brochure - ELA European Lift Association.
WP6-Brochure-E4 brochure - ELA European Lift Association.
WP6-Brochure-E4 brochure - ELA European Lift Association.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
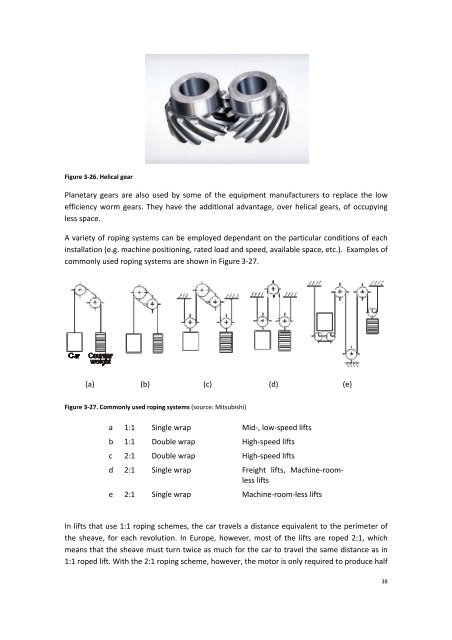
Figure 3‐26. Helical gear<br />
Planetary gears are also used by some of the equipment manufacturers to replace the low<br />
efficiency worm gears. They have the additional advantage, over helical gears, of occupying<br />
less space.<br />
A variety of roping systems can be employed dependant on the particular conditions of each<br />
installation (e.g. machine positioning, rated load and speed, available space, etc.). Examples of<br />
commonly used roping systems are shown in Figure 3‐27.<br />
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)<br />
Figure 3‐27. Commonly used roping systems (source: Mitsubishi)<br />
a 1:1 Single wrap Mid‐, low‐speed lifts<br />
b 1:1 Double wrap High‐speed lifts<br />
c 2:1 Double wrap High‐speed lifts<br />
d 2:1 Single wrap Freight lifts, Machine‐roomless<br />
lifts<br />
e 2:1 Single wrap Machine‐room‐less lifts<br />
In lifts that use 1:1 roping schemes, the car travels a distance equivalent to the perimeter of<br />
the sheave, for each revolution. In Europe, however, most of the lifts are roped 2:1, which<br />
means that the sheave must turn twice as much for the car to travel the same distance as in<br />
1:1 roped lift. With the 2:1 roping scheme, however, the motor is only required to produce half<br />
38