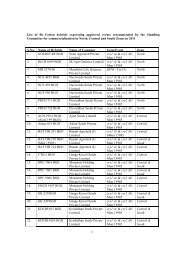
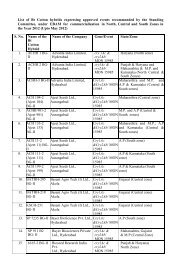
Biosafety Guidelines For Research On Genetically Modified ...
Biosafety Guidelines For Research On Genetically Modified ...
Biosafety Guidelines For Research On Genetically Modified ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
polymerase chain reaction<br />
prion<br />
prokaryotic<br />
promoter<br />
protein<br />
protoplast<br />
receptor<br />
recombinant<br />
recombinant DNA<br />
A technique for generating, in vitro, an increased quantity<br />
of a target segment of DNA.<br />
An infectious agent of unknown etiology which causes<br />
spongiform encephalopathies of humans and animals.<br />
Belonging to the group of microorganisms whose DNA is<br />
not enclosed within a nuclear membrane.<br />
A DNA sequence, located in front of a gene, that controls<br />
expression of the gene. It is the sequence to which RNA<br />
polymerase binds to initiate transcription.<br />
A molecule composed of amino acids.<br />
A plant or bacterial cell which has had the outer cell wall<br />
removed.<br />
Cell-surface protein to which molecules such as hormones<br />
and growth factors bind to exert their effects on the cell, or<br />
to which viruses bind to gain entry to the cell.<br />
Organisms, cells, viruses etc. which contain recombinant<br />
DNA (q.v.).<br />
DNA formed by joining, in vitro, segments of DNA from<br />
different organisms.<br />
recombination The occurrence or production of progeny with<br />
combinations of genes other than those that occurred in<br />
the parents.<br />
replication<br />
retroviral vector<br />
retrovirus<br />
RNA<br />
sharps<br />
shot-gun cloning<br />
Reproduction.<br />
A retrovirus (q.v.) which is used to introduce foreign DNA<br />
into animal cells, usually by replacing part of the viral<br />
genome with the foreign DNA of interest.<br />
A virus that uses the enzyme reverse transcriptase to copy<br />
its RNA genome into DNA, which then integrates into the<br />
host cell genome.<br />
Ribonucleic acid, a molecule similar to DNA, whose<br />
functions include decoding the instructions for protein<br />
synthesis that are carried by the genes; comprises the<br />
genetic material of some viruses.<br />
Sharp laboratory items such as syringe needles, scalpel<br />
and razor blades, and broken glass.<br />
The production of a large random collection of cloned<br />
fragments of the DNA of an organism, from which genes<br />
of interest can later be selected.<br />
Appendix - Page 58