Download Complete PDF - apctt
Download Complete PDF - apctt
Download Complete PDF - apctt
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
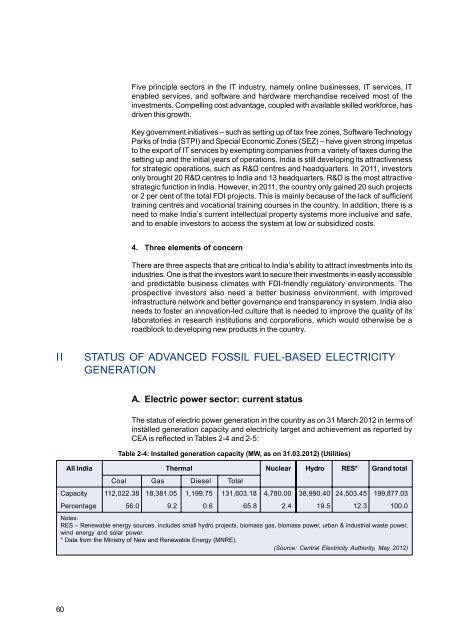
Five principle sectors in the IT industry, namely online businesses, IT services, ITenabled services, and software and hardware merchandise received most of theinvestments. Compelling cost advantage, coupled with available skilled workforce, hasdriven this growth.Key government initiatives – such as setting up of tax free zones, Software TechnologyParks of India (STPI) and Special Economic Zones (SEZ) – have given strong impetusto the export of IT services by exempting companies from a variety of taxes during thesetting up and the initial years of operations. India is still developing its attractivenessfor strategic operations, such as R&D centres and headquarters. In 2011, investorsonly brought 20 R&D centres to India and 13 headquarters. R&D is the most attractivestrategic function in India. However, in 2011, the country only gained 20 such projectsor 2 per cent of the total FDI projects. This is mainly because of the lack of sufficienttraining centres and vocational training courses in the country. In addition, there is aneed to make India’s current intellectual property systems more inclusive and safe,and to enable investors to access the system at low or subsidized costs.4. Three elements of concernThere are three aspects that are critical to India’s ability to attract investments into itsindustries. One is that the investors want to secure their investments in easily accessibleand predictable business climates with FDI-friendly regulatory environments. Theprospective investors also need a better business environment, with improvedinfrastructure network and better governance and transparency in system. India alsoneeds to foster an innovation-led culture that is needed to improve the quality of itslaboratories in research institutions and corporations, which would otherwise be aroadblock to developing new products in the country.IISTATUS OF ADVANCED FOSSIL FUEL-BASED ELECTRICITYGENERATIONA. Electric power sector: current statusThe status of electric power generation in the country as on 31 March 2012 in terms ofinstalled generation capacity and electricity target and achievement as reported byCEA is reflected in Tables 2-4 and 2-5:Table 2-4: Installed generation capacity (MW, as on 31.03.2012) (Utilities)All India Thermal Nuclear Hydro RES* Grand totalCoal Gas Diesel TotalCapacity 112,022.38 18,381.05 1,199.75 131,603.18 4,780.00 38,990.40 24,503.45 199,877.03Percentage 56.0 9.2 0.6 65.8 2.4 19.5 12.3 100.0Notes:RES – Renewable energy sources, includes small hydro projects, biomass gas, biomass power, urban & industrial waste power,wind energy and solar power.* Data from the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).(Source: Central Electricity Authority, May 2012)60