RAINFOR GEM Intensive Plots Manual (pdf) - University of Oxford
RAINFOR GEM Intensive Plots Manual (pdf) - University of Oxford
RAINFOR GEM Intensive Plots Manual (pdf) - University of Oxford
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
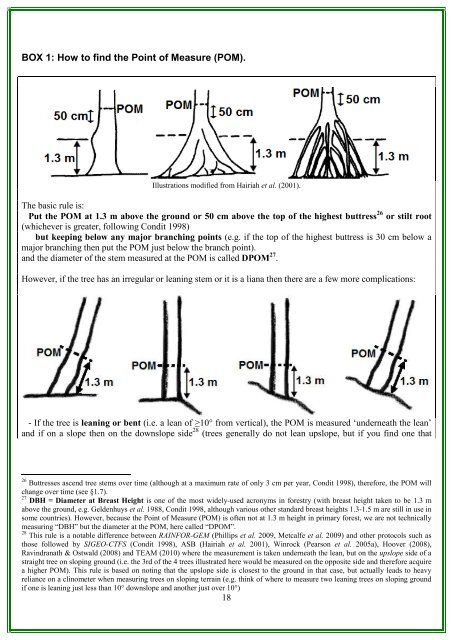
BOX 1: How to find the Point <strong>of</strong> Measure (POM).Illustrations modified from Hairiah et al. (2001).The basic rule is:Put the POM at 1.3 m above the ground or 50 cm above the top <strong>of</strong> the highest buttress 26 or stilt root(whichever is greater, following Condit 1998)but keeping below any major branching points (e.g. if the top <strong>of</strong> the highest buttress is 30 cm below amajor branching then put the POM just below the branch point).and the diameter <strong>of</strong> the stem measured at the POM is called DPOM 27 .However, if the tree has an irregular or leaning stem or it is a liana then there are a few more complications:- If the tree is leaning or bent (i.e. a lean <strong>of</strong> ≥10° from vertical), the POM is measured ‘underneath the lean’and if on a slope then on the downslope side 28 (trees generally do not lean upslope, but if you find one that26 Buttresses ascend tree stems over time (although at a maximum rate <strong>of</strong> only 3 cm per year, Condit 1998), therefore, the POM willchange over time (see §1.7).27 DBH = Diameter at Breast Height is one <strong>of</strong> the most widely-used acronyms in forestry (with breast height taken to be 1.3 mabove the ground, e.g. Geldenhuys et al. 1988, Condit 1998, although various other standard breast heights 1.3-1.5 m are still in use insome countries). However, because the Point <strong>of</strong> Measure (POM) is <strong>of</strong>ten not at 1.3 m height in primary forest, we are not technicallymeasuring “DBH” but the diameter at the POM, here called “DPOM”.28 This rule is a notable difference between <strong>RAINFOR</strong>-<strong>GEM</strong> (Phillips et al. 2009, Metcalfe et al. 2009) and other protocols such asthose followed by SIGEO-CTFS (Condit 1998), ASB (Hairiah et al. 2001), Winrock (Pearson et al. 2005a), Hoover (2008),Ravindranath & Ostwald (2008) and TEAM (2010) where the measurement is taken underneath the lean, but on the upslope side <strong>of</strong> astraight tree on sloping ground (i.e. the 3rd <strong>of</strong> the 4 trees illustrated here would be measured on the opposite side and therefore acquirea higher POM). This rule is based on noting that the upslope side is closest to the ground in that case, but actually leads to heavyreliance on a clinometer when measuring trees on sloping terrain (e.g. think <strong>of</strong> where to measure two leaning trees on sloping groundif one is leaning just less than 10° downslope and another just over 10°)18