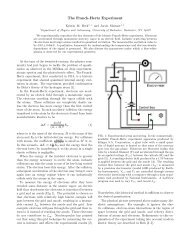
coulomb excitation data analysis codes; gosia 2007 - Physics and ...
coulomb excitation data analysis codes; gosia 2007 - Physics and ...
coulomb excitation data analysis codes; gosia 2007 - Physics and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
q (20)s (0 + → 2 + ) · M 1 ζ (20)0 + 2 + = qq (20)a (0 + → 2 + ) · M 1 ζ (20)0 + 2 + = q 1 (3.11)q (20)s (2 + → 2 + ) · M 2 ζ (20)2 + 2 + = QNote that there is no antisymmetric component of the interaction for the quadrupole moment, sinceζ =0.The A matrices can then be written as:µ 0 −q1A 1 =(3.12)q 1 0µ 0 qA 2 =q Qyielding:µ cos q1 ¯+sinqexp(±A 1 )=1(3.13)± sin q 1 cos q 1Ãcos p −1exp(−iA 2 )=e iQ/2 2 i Q p sin p − iq p sin p!− iq p sin p cos p + 1 2 i Q p sin pwhereUsing 3.5 gives:p = 1 2 (Q2 +4q 2 ) 1/2a 2 + = 1 sin pieiQ/22 p (Q sin 2q 1 − 2q cos 2q 1 ) (3.14)which results in an <strong>excitation</strong> probability:P 2+ = 1 sin 2 p4 p 2 (Q sin 2q 1 − 2q cos 2q 1 ) 2 (3.15)The formula 3.15 is a generalization of the second-order perturbation theory result. Taking into accountonly the lowest order terms in q, q 1 ,q 1 <strong>and</strong> Q gives:P 2+ ≈ q 2 (1 − Q · q1q )2 (3.16)as predicted by second-order perturbation theory. It should be observed, that the influence of the quadrupolemoment is significant only if the ratio of antisymmetric to symmetric q parameters is high, which physicallycorresponds to a large value of ξ. As can be seen from 3.14, theprimaryeffect of the static moment is rotationof the complex <strong>excitation</strong> amplitude, due to the exp(iQ/2) factor. This allows rather accurate measurementsof static moments in cases of interfering paths of <strong>excitation</strong>, i.e., when a state is excited in a comparable wayvia two or more sequences of couplings. In this situation the phases that the partial <strong>excitation</strong> amplitudesare summed are of primary importance.In general, 3.10 is only a semianalytical formula, since for complex cases, exponents of the A matricesmust be evaluated numerically. Nevertheless, numerical determination of exp(A) operators is much fasterthan the integration of a system of differential equations. Application of the A matrix approximation forfitting of matrix elements to reproduce experimental <strong>data</strong> will be discussed in some more detail in Chapter4. It is worth observing that the truncation of Taylor series approximating the exp(A) operators providesa way to generate perturbation theory of a given order, thus being useful for investigating weak <strong>excitation</strong>processes.33