Proceedings Fonetik 2009 - Institutionen för lingvistik
Proceedings Fonetik 2009 - Institutionen för lingvistik
Proceedings Fonetik 2009 - Institutionen för lingvistik
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
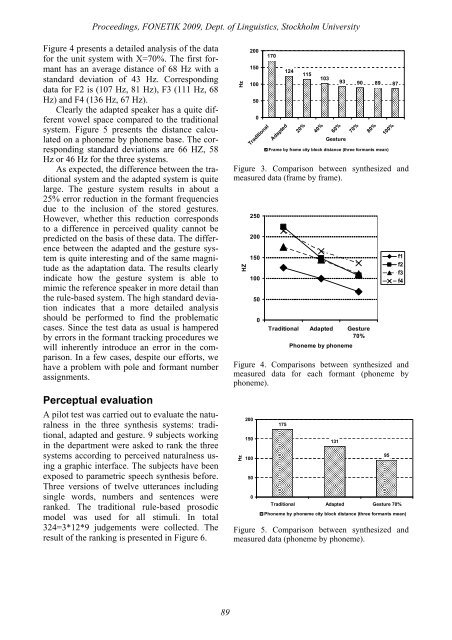
<strong>Proceedings</strong>, FONETIK <strong>2009</strong>, Dept. of Linguistics, Stockholm UniversityFigure 4 presents a detailed analysis of the datafor the unit system with X=70%. The first formanthas an average distance of 68 Hz with astandard deviation of 43 Hz. Correspondingdata for F2 is (107 Hz, 81 Hz), F3 (111 Hz, 68Hz) and F4 (136 Hz, 67 Hz).Clearly the adapted speaker has a quite differentvowel space compared to the traditionalsystem. Figure 5 presents the distance calculatedon a phoneme by phoneme base. The correspondingstandard deviations are 66 HZ, 58Hz or 46 Hz for the three systems.As expected, the difference between the traditionalsystem and the adapted system is quitelarge. The gesture system results in about a25% error reduction in the formant frequenciesdue to the inclusion of the stored gestures.However, whether this reduction correspondsto a difference in perceived quality cannot bepredicted on the basis of these data. The differencebetween the adapted and the gesture systemis quite interesting and of the same magnitudeas the adaptation data. The results clearlyindicate how the gesture system is able tomimic the reference speaker in more detail thanthe rule-based system. The high standard deviationindicates that a more detailed analysisshould be performed to find the problematiccases. Since the test data as usual is hamperedby errors in the formant tracking procedures wewill inherently introduce an error in the comparison.In a few cases, despite our efforts, wehave a problem with pole and formant numberassignments.Perceptual evaluationA pilot test was carried out to evaluate the naturalnessin the three synthesis systems: traditional,adapted and gesture. 9 subjects workingin the department were asked to rank the threesystems according to perceived naturalness usinga graphic interface. The subjects have beenexposed to parametric speech synthesis before.Three versions of twelve utterances includingsingle words, numbers and sentences wereranked. The traditional rule-based prosodicmodel was used for all stimuli. In total324=3*12*9 judgements were collected. Theresult of the ranking is presented in Figure 6.Hz200150100500Traditional170Adapted12420%11510340%60%Gesture93 90 89 8770%80%Frame by frame city block distance (three formants mean)100%Figure 3. Comparison between synthesized andmeasured data (frame by frame).HZ250200150100500Traditional Adapted Gesture70%Phoneme by phonemeFigure 4. Comparisons between synthesized andmeasured data for each formant (phoneme byphoneme).Hz200150100500175131Traditional Adapted Gesture 70%95f1f2f3f4Phoneme by phoneme city block distance (three formants mean)Figure 5. Comparison between synthesized andmeasured data (phoneme by phoneme).89