- Page 2: Copyright information Permission ha
- Page 5 and 6: Preface Health, United States, 2014
- Page 7 and 8: Accessing Health, United States Hea
- Page 9 and 10: Contents
- Page 11 and 12: Trend Tables Health Status and Dete
- Page 13 and 14: Figure 28. Prescription drug use in
- Page 15 and 16: List of Trend Tables Health Status
- Page 17 and 18: Table 64. Healthy weight, overweigh
- Page 19 and 20: State Health Expenditures and Healt
- Page 21 and 22: Health, United States, 2014: At a G
- Page 23 and 24: Highlights This section presents se
- Page 25 and 26: Use of Preventive Medical Care Serv
- Page 27 and 28: Chartbook: Figures 1-19
- Page 29 and 30: Mortality Selected Causes of Death
- Page 31 and 32: Disability Measures Basic Actions D
- Page 33 and 34: Health Risk Factors Overweight and
- Page 35 and 36: Health Insurance Coverage Among Adu
- Page 37 and 38: Personal Health Care Expenditures M
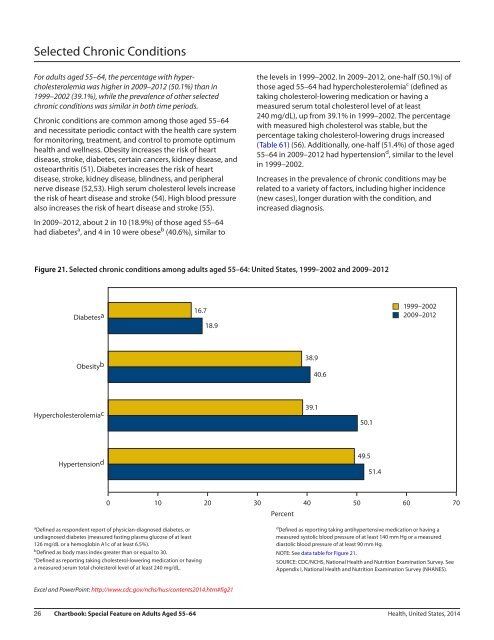
- Page 39 and 40: Special Feature on Adults Aged 55-6
- Page 41: Health, United States, 2014: Profil
- Page 45 and 46: Current Cigarette Smoking In 2012-2
- Page 47 and 48: Health Insurance Coverage For adult
- Page 49 and 50: Use of Preventive Services and Scre
- Page 51 and 52: Delay or Nonreceipt of Medical Care
- Page 53 and 54: Data table for Figure 20. Death rat
- Page 55 and 56: Data table for Figure 22. Serious o
- Page 57 and 58: Data table for Figure 24. Participa
- Page 59 and 60: Data table for Figure 26. Health ca
- Page 61 and 62: Data table for Figure 28. Prescript
- Page 63 and 64: Technical Notes Data Sources and Co
- Page 65 and 66: 26. Martinez ME, Cohen RA. Health i
- Page 67 and 68: 83. CDC. Vaccine recommendations of
- Page 69 and 70: Table 1 (page 1 of 3). Resident pop
- Page 71 and 72: Table 1 (page 3 of 3). Resident pop
- Page 73 and 74: Table 2 (page 2 of 2). Persons belo
- Page 75 and 76: Table 3 (page 2 of 3). Crude birth
- Page 77 and 78: Table 4 (page 1 of 2). Teenage chil
- Page 79 and 80: Table 5. Nonmarital childbearing, b
- Page 81 and 82: Table 7 (page 1 of 3). Low birthwei
- Page 83 and 84: Table 7 (page 3 of 3). Low birthwei
- Page 85 and 86: Table 9 (page 1 of 6). Contraceptiv
- Page 87 and 88: Table 9 (page 3 of 6). Contraceptiv
- Page 89 and 90: Table 9 (page 5 of 6). Contraceptiv
- Page 91 and 92: Table 10. Breastfeeding among mothe
- Page 93 and 94:
Table 11 (page 2 of 2). Infant, neo
- Page 95 and 96:
Table 13 (page 1 of 3). Infant mort
- Page 97 and 98:
Table 13 (page 3 of 3). Infant mort
- Page 99 and 100:
Table 15 (page 1 of 2). Life expect
- Page 101 and 102:
Table 16 (page 1 of 2). Life expect
- Page 103 and 104:
Table 17 (page 1 of 2). Age-adjuste
- Page 105 and 106:
Table 18 (page 1 of 4). Age-adjuste
- Page 107 and 108:
Table 18 (page 3 of 4). Age-adjuste
- Page 109 and 110:
Table 19 (page 1 of 4). Years of po
- Page 111 and 112:
Table 19 (page 3 of 4). Years of po
- Page 113 and 114:
Table 20 (page 1 of 4). Leading cau
- Page 115 and 116:
Table 20 (page 3 of 4). Leading cau
- Page 117 and 118:
Table 21 (page 1 of 2). Leading cau
- Page 119 and 120:
Table 22 (page 1 of 3). Age-adjuste
- Page 121 and 122:
Table 22 (page 3 of 3). Age-adjuste
- Page 123 and 124:
Table 23 (page 2 of 4). Death rates
- Page 125 and 126:
Table 23 (page 4 of 4). Death rates
- Page 127 and 128:
Table 24 (page 2 of 3). Death rates
- Page 129 and 130:
Table 25 (page 1 of 3). Death rates
- Page 131 and 132:
Table 25 (page 3 of 3). Death rates
- Page 133 and 134:
Table 26 (page 2 of 4). Death rates
- Page 135 and 136:
Table 26 (page 4 of 4). Death rates
- Page 137 and 138:
Table 27 (page 2 of 3). Death rates
- Page 139 and 140:
Table 28 (page 1 of 2). Death rates
- Page 141 and 142:
Table 29 (page 1 of 2). Death rates
- Page 143 and 144:
Table 30 (page 1 of 3). Death rates
- Page 145 and 146:
Table 30 (page 3 of 3). Death rates
- Page 147 and 148:
Table 31 (page 2 of 4). Death rates
- Page 149 and 150:
Table 31 (page 4 of 4). Death rates
- Page 151 and 152:
Table 32 (page 2 of 4). Death rates
- Page 153 and 154:
Table 32 (page 4 of 4). Death rates
- Page 155 and 156:
Table 33 (page 2 of 3). Death rates
- Page 157 and 158:
Table 34 (page 1 of 3). Death rates
- Page 159 and 160:
Table 34 (page 3 of 3). Death rates
- Page 161 and 162:
Table 36 (page 1 of 2). Occupationa
- Page 163 and 164:
Table 37 (page 1 of 2). Selected no
- Page 165 and 166:
Table 38 (page 1 of 2). Human immun
- Page 167 and 168:
Table 39 (page 1 of 5). Health cond
- Page 169 and 170:
Table 39 (page 3 of 5). Health cond
- Page 171 and 172:
Table 39 (page 5 of 5). Health cond
- Page 173 and 174:
Table 40 (page 2 of 4). Age-adjuste
- Page 175 and 176:
Table 40 (page 4 of 4). Age-adjuste
- Page 177 and 178:
Table 42 (page 1 of 2). Respondent-
- Page 179 and 180:
Table 43 (page 1 of 2). Number of r
- Page 181 and 182:
Table 44 (page 1 of 2). Diabetes pr
- Page 183 and 184:
Table 45 (page 1 of 2). End-stage r
- Page 185 and 186:
Table 46 (page 1 of 3). Severe head
- Page 187 and 188:
Table 46 (page 3 of 3). Severe head
- Page 189 and 190:
Table 47 (page 2 of 2). Disability
- Page 191 and 192:
Table 48 (page 2 of 2). Vision limi
- Page 193 and 194:
Table 49 (page 2 of 2). Hearing lim
- Page 195 and 196:
Table 50 (page 2 of 2). Respondent-
- Page 197 and 198:
Table 51 (page 2 of 2). Serious psy
- Page 199 and 200:
Table 52 (page 2 of 2). Current cig
- Page 201 and 202:
Table 54 (page 1 of 3). Current cig
- Page 203 and 204:
Table 54 (page 3 of 3). Current cig
- Page 205 and 206:
Table 55 (page 2 of 2). Use of sele
- Page 207 and 208:
Table 56 (page 2 of 3). Use of sele
- Page 209 and 210:
Table 57 (page 1 of 3). Health risk
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 57 (page 3 of 3). Health risk
- Page 213 and 214:
Table 58 (page 2 of 3). Heavier dri
- Page 215 and 216:
Table 59 (page 1 of 2). Selected he
- Page 217 and 218:
Table 60 (page 1 of 2). Hypertensio
- Page 219 and 220:
Table 61 (page 1 of 4). Cholesterol
- Page 221 and 222:
Table 61 (page 3 of 4). Cholesterol
- Page 223 and 224:
Table 62 (page 1 of 2). Mean macron
- Page 225 and 226:
Table 63 (page 1 of 5). Participati
- Page 227 and 228:
Table 63 (page 3 of 5). Participati
- Page 229 and 230:
Table 63 (page 5 of 5). Participati
- Page 231 and 232:
Table 64 (page 2 of 7). Healthy wei
- Page 233 and 234:
Table 64 (page 4 of 7). Healthy wei
- Page 235 and 236:
Table 64 (page 6 of 7). Healthy wei
- Page 237 and 238:
Table 65 (page 1 of 2). Obesity amo
- Page 239 and 240:
Table 66 (page 1 of 2). Untreated d
- Page 241 and 242:
Table 67 (page 1 of 2). No usual so
- Page 243 and 244:
Table 68 (page 1 of 2). No usual so
- Page 245 and 246:
Table 69 (page 1 of 3). Delay or no
- Page 247 and 248:
Table 69 (page 3 of 3). Delay or no
- Page 249 and 250:
Table 70 (page 2 of 2). No health c
- Page 251 and 252:
Table 71 (page 2 of 3). Health care
- Page 253 and 254:
Table 72 (page 1 of 3). Vaccination
- Page 255 and 256:
Table 72 (page 3 of 3). Vaccination
- Page 257 and 258:
Table 74 (page 1 of 2). Influenza v
- Page 259 and 260:
Table 75 (page 1 of 2). Pneumococca
- Page 261 and 262:
Table 76 (page 1 of 3) . Use of mam
- Page 263 and 264:
Table 76 (page 3 of 3). Use of mamm
- Page 265 and 266:
Table 77 (page 2 of 5). Use of Pap
- Page 267 and 268:
Table 77 (page 4 of 5). Use of Pap
- Page 269 and 270:
Table 78 (page 1 of 2). Use of colo
- Page 271 and 272:
Table 79 (page 1 of 4). Emergency d
- Page 273 and 274:
Table 79 (page 3 of 4). Emergency d
- Page 275 and 276:
Table 80 (page 1 of 3). Emergency d
- Page 277 and 278:
Table 80 (page 3 of 3). Emergency d
- Page 279 and 280:
Table 81 (page 2 of 2). Initial inj
- Page 281 and 282:
Table 82 (page 2 of 3). Visits to p
- Page 283 and 284:
Table 83 (page 1 of 2). Visits to p
- Page 285 and 286:
Table 84 (page 1 of 2) . Dental vis
- Page 287 and 288:
Table 85 (page 1 of 2). Prescriptio
- Page 289 and 290:
Table 86 (page 1 of 3). Selected pr
- Page 291 and 292:
Table 86 (page 3 of 3). Selected pr
- Page 293 and 294:
Table 87 (page 2 of 4). Persons wit
- Page 295 and 296:
Table 87 (page 4 of 4). Persons wit
- Page 297 and 298:
Table 88 (page 2 of 3). Discharges,
- Page 299 and 300:
Table 89 (page 1 of 3). Discharge r
- Page 301 and 302:
Table 89 (page 3 of 3). Discharge r
- Page 303 and 304:
Table 90 (page 2 of 4). Discharges
- Page 305 and 306:
Table 90 (page 4 of 4). Discharges
- Page 307 and 308:
Table 92. Active physicians and phy
- Page 309 and 310:
Table 94. Doctors of medicine in pr
- Page 311 and 312:
Table 96. Healthcare employment and
- Page 313 and 314:
Table 98. Hospitals, beds, and occu
- Page 315 and 316:
Table 100. Occupancy rates in commu
- Page 317 and 318:
Table 101 (page 2 of 2). Nursing ho
- Page 319 and 320:
Table 102 (page 2 of 2). Gross dome
- Page 321 and 322:
Table 103 (page 2 of 2). National h
- Page 323 and 324:
Table 104 (page 2 of 3). Personal h
- Page 325 and 326:
Table 105 (page 1 of 3). Cost of ho
- Page 327 and 328:
Table 105 (page 3 of 3). Cost of ho
- Page 329 and 330:
Table 106 (page 2 of 3). Expenses f
- Page 331 and 332:
Table 107 (page 1 of 3). Sources of
- Page 333 and 334:
Table 107 (page 3 of 3). Sources of
- Page 335 and 336:
Table 109 (page 1 of 2). National h
- Page 337 and 338:
Table 110. Employers' costs per emp
- Page 339 and 340:
Table 111 (page 2 of 3). Private he
- Page 341 and 342:
Table 112 (page 1 of 3). Private he
- Page 343 and 344:
Table 112 (page 3 of 3). Private he
- Page 345 and 346:
Table 113 (page 2 of 3). Medicaid c
- Page 347 and 348:
Table 114 (page 1 of 3). No health
- Page 349 and 350:
Table 114 (page 3 of 3). No health
- Page 351 and 352:
Table 115 (page 2 of 2). Health ins
- Page 353 and 354:
Table 116 (page 2 of 2). Medicare e
- Page 355 and 356:
Table 117 (page 2 of 2). Medicare b
- Page 357 and 358:
Table 118 (page 2 of 2). Medicaid b
- Page 359 and 360:
Table 120. Department of Veterans A
- Page 361 and 362:
Table 121 (page 2 of 2). Medicare e
- Page 363 and 364:
Table 123 (page 1 of 3). Persons un
- Page 365 and 366:
Table 123 (page 3 of 3). Persons un
- Page 367 and 368:
Appendix Contents Appendix I. Data
- Page 369 and 370:
Mammography .......................
- Page 371 and 372:
Appendix I. Data Sources Health, Un
- Page 373 and 374:
institutional group quarters popula
- Page 375 and 376:
entire survey. In addition, some of
- Page 377 and 378:
Another source of Medicaid informat
- Page 379 and 380:
For More Information. See the CMS R
- Page 381 and 382:
Sample data are weighted to produce
- Page 383 and 384:
The estimation procedure used to pr
- Page 385 and 386:
with the Armed Forces (although the
- Page 387 and 388:
areas. EDs are treated as their own
- Page 389 and 390:
Methodology. NIS is a nationwide te
- Page 391 and 392:
National Notifiable Diseases Survei
- Page 393 and 394:
interviewing (ACASI), are used to p
- Page 395 and 396:
Coverage. Data presented in Health,
- Page 397 and 398:
Heron M, Hoyert DL, Murphy SL, et a
- Page 399 and 400:
specified rules for the collection,
- Page 401 and 402:
Quality Improvement Evaluation Syst
- Page 403 and 404:
information on treatment and payer
- Page 405 and 406:
Reference American Dental Associati
- Page 407 and 408:
For More Information. See The Guttm
- Page 409 and 410:
Table I. United States projected ye
- Page 411 and 412:
males and black females in 1950 are
- Page 413 and 414:
hypertension. Those with uncontroll
- Page 415 and 416:
Table IV. Cause-of-death codes, by
- Page 417 and 418:
High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (A
- Page 419 and 420:
Table V. Comparability of selected
- Page 421 and 422:
Dental caries was identified by an
- Page 423 and 424:
For more information on prescriptio
- Page 425 and 426:
public-use data release. NCHS. 2014
- Page 427 and 428:
Figure I. U.S. Census Bureau: Four
- Page 429 and 430:
with only Indian Health Service (IH
- Page 431 and 432:
Table VII. Percentage of persons un
- Page 433 and 434:
analytic purposes. See: NAACCR guid
- Page 435 and 436:
cause of death in ICD-9. The asteri
- Page 437 and 438:
Table IX. Codes for external causes
- Page 439 and 440:
U.S. life tables by Hispanic origin
- Page 441 and 442:
for Healthcare Research and Quality
- Page 443 and 444:
Affordable Care Act Provides Eligib
- Page 445 and 446:
Micropolitan statistical area—The
- Page 447 and 448:
In 2000 and 2003, women were asked
- Page 449 and 450:
see Appendix I, Population Census a
- Page 451 and 452:
Table XII. Codes for procedure cate
- Page 453 and 454:
Table XIV. Private health care cove
- Page 455 and 456:
the extent that race and Hispanic o
- Page 457 and 458:
Perinatal mortality rates and ratio
- Page 459 and 460:
coverage are considered uninsured.
- Page 461 and 462:
Index
- Page 463 and 464:
A—Con. Table/Figure (F) Asian or
- Page 465 and 466:
D Table/Figure (F) Deaths, death ra
- Page 467 and 468:
H—Con. Table/Figure (F) Hispanic
- Page 469 and 470:
M—Con. Table/Figure (F) Metropoli
- Page 471 and 472:
S Table/Figure (F) Salmonellosis, s