n - PATh :.: Process and Product Applied Thermodynamics research ...
n - PATh :.: Process and Product Applied Thermodynamics research ...
n - PATh :.: Process and Product Applied Thermodynamics research ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Modeling<br />
The equation of state is written in terms of the Helmholtz free energy. The different<br />
microscopic contributions that control the macroscopic properties of the fluid are explicitly<br />
considered when building the theory. The residual Helmholtz free energy for an<br />
n-component mixture of associating chain molecules can be expressed as a sum of three<br />
terms: a reference term, A ref , including the repulsive <strong>and</strong> the attractive energies, a chain<br />
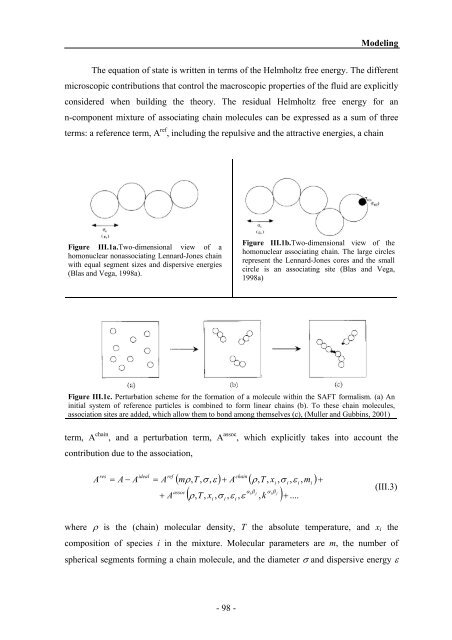
Figure III.1a.Two-dimensional view of a<br />
homonuclear nonassociating Lennard-Jones chain<br />
with equal segment sizes <strong>and</strong> dispersive energies<br />
(Blas <strong>and</strong> Vega, 1998a).<br />
Figure III.1b.Two-dimensional view of the<br />
homonuclear associating chain. The large circles<br />
represent the Lennard-Jones cores <strong>and</strong> the small<br />
circle is an associating site (Blas <strong>and</strong> Vega,<br />
1998a)<br />
Figure III.1c. Perturbation scheme for the formation of a molecule within the SAFT formalism. (a) An<br />
initial system of reference particles is combined to form linear chains (b). To these chain molecules,<br />
association sites are added, which allow them to bond among themselves (c), (Muller <strong>and</strong> Gubbins, 2001)<br />
term, A chain , <strong>and</strong> a perturbation term, A assoc , which explicitly takes into account the<br />
contribution due to the association,<br />
A<br />
res<br />
= A − A<br />
ideal<br />
= A<br />
ref<br />
+ A<br />
chain<br />
( mρ,<br />
T,<br />
σ , ε ) + A ( ρ,<br />
T,<br />
x , σ , ε , m )<br />
assoc<br />
αi<br />
β j αi<br />
β j<br />
( ρ,<br />
T,<br />
x , σ , ε , ε , k ) + ....<br />
i<br />
i<br />
i<br />
i<br />
i<br />
i<br />
i<br />
+<br />
(III.3)<br />
where ρ is the (chain) molecular density, T the absolute temperature, <strong>and</strong> xi the<br />
composition of species i in the mixture. Molecular parameters are m, the number of<br />
spherical segments forming a chain molecule, <strong>and</strong> the diameter σ <strong>and</strong> dispersive energy ε<br />
- 98 -