n - PATh :.: Process and Product Applied Thermodynamics research ...
n - PATh :.: Process and Product Applied Thermodynamics research ...
n - PATh :.: Process and Product Applied Thermodynamics research ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Experimental Methods, Results <strong>and</strong> Discussion<br />
solvent <strong>and</strong> the control of the temperature of the entire system in order to avoid<br />
condensation of the vapor.<br />
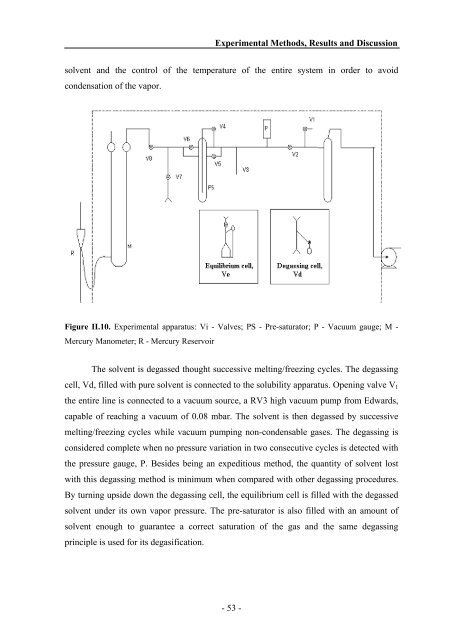
Figure II.10. Experimental apparatus: Vi - Valves; PS - Pre-saturator; P - Vacuum gauge; M -<br />
Mercury Manometer; R - Mercury Reservoir<br />
The solvent is degassed thought successive melting/freezing cycles. The degassing<br />
cell, Vd, filled with pure solvent is connected to the solubility apparatus. Opening valve V1<br />
the entire line is connected to a vacuum source, a RV3 high vacuum pump from Edwards,<br />
capable of reaching a vacuum of 0.08 mbar. The solvent is then degassed by successive<br />
melting/freezing cycles while vacuum pumping non-condensable gases. The degassing is<br />
considered complete when no pressure variation in two consecutive cycles is detected with<br />
the pressure gauge, P. Besides being an expeditious method, the quantity of solvent lost<br />
with this degassing method is minimum when compared with other degassing procedures.<br />
By turning upside down the degassing cell, the equilibrium cell is filled with the degassed<br />
solvent under its own vapor pressure. The pre-saturator is also filled with an amount of<br />
solvent enough to guarantee a correct saturation of the gas <strong>and</strong> the same degassing<br />
principle is used for its degasification.<br />
- 53 -