Tema 3: Resolución de sistemas mediante determinantes
Tema 3: Resolución de sistemas mediante determinantes
Tema 3: Resolución de sistemas mediante determinantes
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
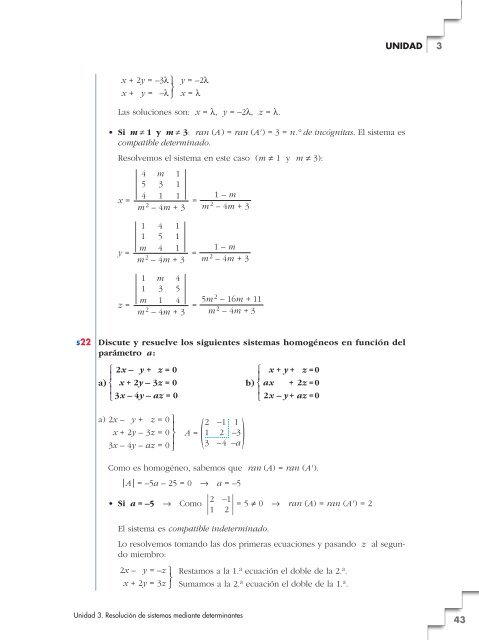
°¢£°§¢§£UNIDAD3x + 2y = –3lx + y = –ly = –2lx = lLas soluciones son: x = l, y = –2l, z = l.• Si m ? 1 y m ? 3: ran (A) = ran (A') = 3 = n.° <strong>de</strong> incógnitas. El sistema escompatible <strong>de</strong>terminado.Resolvemos el sistema en este caso (m ? 1 y m ? 3):4 m 15 3 1§ 4 1 1 §x = =m 2 – 4m + 31 4 11 5 1§ m 4 1 §y = =m 2 – 4m + 31 m 41 3 5§ m 1 4 §z = =m 2 – 4m + 31 – mm 2 – 4m + 31 – mm 2 – 4m + 35m 2 – 16m +11m 2 – 4m +3s22Discute y resuelve los siguientes <strong>sistemas</strong> homogéneos en función <strong>de</strong>lparámetro a:° 2x – y + z = 0° x + y + z =0§§a) ¢ x + 2y –3z = 0b) ¢ ax +2z =0§§£ 3x – 4y – az = 0£ 2x – y + az =0a) 2x – y + z = 0x + 2y –3z = 03x – 4y – az = 0A =2 –1 1)1 2 –3(3 –4 –aComo es homogéneo, sabemos que ran (A) = ran (A').| A | = –5a – 25 = 0 8 a = –52 –1• Si a = –5 8 Como | | = 5 ? 0 8 ran (A) = ran (A') = 21 2El sistema es compatible in<strong>de</strong>terminado.Lo resolvemos tomando las dos primeras ecuaciones y pasando z al segundomiembro:2x – y = –zx + 2y = 3z°¢£Restamos a la 1. a ecuación el doble <strong>de</strong> la 2. a .Sumamos a la 2. a ecuación el doble <strong>de</strong> la 1. a .Unidad 3. <strong>Resolución</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>sistemas</strong> <strong>mediante</strong> <strong>de</strong>terminantes43