Last ned i fulltekst - Sifo
Last ned i fulltekst - Sifo
Last ned i fulltekst - Sifo
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
14<br />
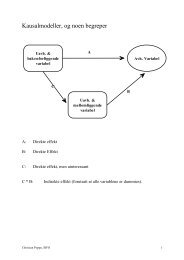
Prismarginer for kjøtt 1989-1999<br />
the meat-industry including distribution, and lastly the retailer. These prices<br />
were mapped for selected products during the period from 1989-1999. We<br />
have thus obtai<strong>ned</strong> a pattern of mark-ups in the distribution channel over time.<br />
By using these estimates, we have been able to follow potential changes in<br />
the gross mark-ups over time. This is a straight mapping study and it will not<br />
say anything about the reasons for the changes that we see. However, by<br />
looking at the changes in mark-ups over time, we have made a basis for further<br />
discussions on what has caused the changes we see. The margin estimates<br />
will then be a good basis for further analyses, which are necessary in<br />
order to explain which processes have caused the changes in the price structure.<br />
Changes in the external conditions and structure of the value chain of<br />
meat products<br />
Our estimates on meat products reach from 1989 until 1999. This period was<br />
in many ways a very turbulent time for the foodstuff system. During this period,<br />
significant changes in the external conditions for the production of meat<br />
products took place. One important change in agriculture politics was the<br />
transition from price-supports to direct payments. The changes in milk quotas,<br />
involving, among other things, the introduction of marketable milk quotas and<br />
a decrease in milk production, have also had an effect on the meat segment.<br />
In addition, there have been changes in the external conditions regarding<br />
trade politics. After the latest Uruguay-round, the possibilities of using export<br />
to regulate the domestic market were severely limited, and the introduction of<br />
customs tariff rates have ope<strong>ned</strong> up the possibility for more imports in the future.<br />
The largest operator in Norwegian meat production, Norsk Kjøtt, has changed<br />
its organisation structure in order to meet the changes in the external conditions<br />
and the competitive market. For the private meat industry, the period has<br />
been a difficult one financially. The processing links have also gone through<br />
severe changes, not least because of changes further down the chain. The<br />
development of ‘Leiv Vidar’ and the turnover of hot dogs at petrol stations are<br />
good examples. The introduction of ”private labels” in the chain stores has<br />
also been a challenge for the business.<br />
In the 1980s and 90s, retail and wholesale companies in Norway went<br />
through great changes. The establishment of discount shops in the 80s led to<br />
a greater focus on the purchasing terms for the grocery business. The lowprice<br />
chains expanded quickly, and as a response to this, the independent<br />
shops established purchasing collaborations. At the end of the 1990s, four<br />
groupings control 99% of the grocery market.