JAHRESBERICHT - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion - ETH Zürich
JAHRESBERICHT - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion - ETH Zürich
JAHRESBERICHT - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion - ETH Zürich
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
FORSCHUNG<br />
Generische Brandrisikoberechnung von<br />
Wohn- <strong>und</strong> Industriegebäuden<br />
Projektleitung: Prof. Dr. M. Fontana<br />
Prof. Dr. M.H. Faber<br />
Mitarbeiter: G. De Sanctis, Dr. J. Köhler<br />
Projektpartner: Vereinigung Kantonaler<br />
Feuerversicherungen (VKF)<br />
Das Ziel des Brandschutzes ist die Unversehrtheit<br />
des Menschen zu bewahren (Personenschutz) <strong>und</strong><br />
Sach schäden möglichst zu vermeiden (Sach wert -<br />
schutz). Der Brandschutz wird sowohl durch vor -<br />
beu gende als auch durch abwehrende Brand schutz -<br />
mass nahmen umgesetzt. Diese Massnahmen können<br />
im Kontext von Brandschutzmanagement als<br />
Handlungsalternativen aufgefasst werden. Da sich<br />
Brände kaum vollständig vermeiden lassen, können<br />
immer gewisse Konsequenzen erwartet werden.<br />
Die erwartete Grösse der Konsequenzen entspricht<br />
dem Brandrisiko <strong>und</strong> kann durch Brand schutz mass -<br />
nah men beeinflusst werden.<br />
Jede Brandschutzmassnahme ist mit Kosten verb<strong>und</strong>en<br />
<strong>und</strong> führt zu einer entsprechenden Ri si ko re -<br />
duk tion, die als Nutzen aufgefasst werden kann.<br />
Falls im Brandschutzkonzept die Anforderungen<br />
bezüglich des Personenschutzes eingehalten werden,<br />
so ist es vernünftig Kosten <strong>und</strong> Nutzen von<br />
Brand schutzmassnahmen zu vergleichen. Dies führt<br />
zu einer ökonomischen Optimierung der Ge samt -<br />
kosten <strong>und</strong> führt zur Wahl einer effizienten Brand -<br />
schutzmassnahme unter Be rück sich ti gung der<br />
Personensicherheit als auch des Sach wert schutzes.<br />
Um effiziente Massnahmen zu bestimmen ist eine<br />
generische <strong>und</strong> quantitative Brand ri si ko be rech nung<br />
erforderlich.<br />
Die generische Brandrisikoberechnung ermöglicht<br />
die Quantifizierung der erwarteten Kon se quen -<br />
zen eines Brandes in Abhängigkeit von Ri si ko in -<br />
dikatoren <strong>und</strong> Brandschutzmassnahmen. Sowohl die<br />
Indikatoren als auch die Massnahmen können mit<br />
Unsicherheiten behaftet sein, da der In for ma tions -<br />
gehalt der Parameter unvollständig ist oder weil sie<br />
na türlich variieren. Eine probabilistische Mo del lie -<br />
rung ermöglicht eine konsistente Be rück sich tigung<br />
die ser Unsicherheiten sowie die Re prä sen tation der<br />
physikalischen Prozesse eines Bran des.<br />
Generic fire risk assessment in residential<br />
and industrial buildings<br />
The aim of fire safety engineering is to reduce the<br />
con sequences, i.e. human and financial losses, as<br />
much as reasonably possible. Fire safety can be in -<br />
cre ased by passive and active fire safety measures.<br />
These measures can be regarded as decision alternatives<br />
in the context of fire safety management. Be cause<br />
fires cannot be avoided completely, certain consequences<br />
always have to be anticipated. The expected<br />
value of the consequences corresponds to the fire risk<br />
and can be influenced by fire safety measures.<br />
Every measure is associated with costs and, if<br />
related to the corresponding risk reductions, a certain<br />
benefit. If the acceptability of fire safety design<br />
in terms of risk to life is fulfilled, then it is reasonable<br />
to compare the costs of fire safety measures<br />
with its benefits, i.e. to perform an economic optimization<br />
of the overall costs. This is leading to a<br />
choice of efficient fire safety measures regarding<br />
risk to life as well as financial losses. To compare<br />
and select efficient measures a generic and quantitative<br />
fire risk assessment method is required.<br />
Generic risk assessment facilitates quantifica -<br />
tion of the expected values of consequences due to<br />
fire events in dependence of risk indicators and fire<br />
safety measures. Both may be associates with<br />
uncertainties due to lack of knowledge and randomness.<br />
A probabilistic model allows to consider these<br />
uncertainties consistently and to represent the physical<br />
processes of a fire hazard.<br />
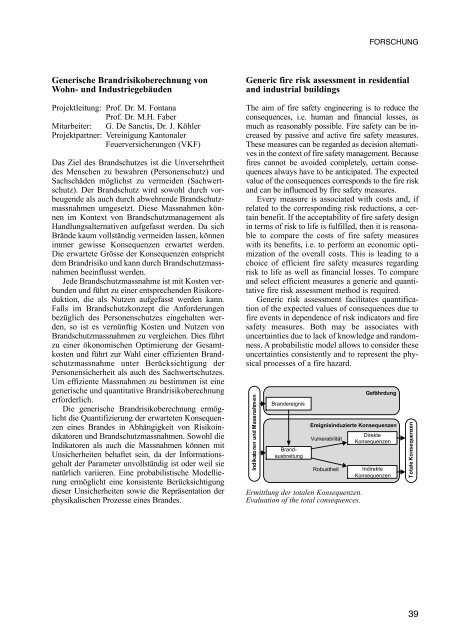
Ermittlung der totalen Konsequenzen.<br />
Evaluation of the total consequences.<br />
39