JAHRESBERICHT - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion - ETH Zürich
JAHRESBERICHT - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion - ETH Zürich
JAHRESBERICHT - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion - ETH Zürich
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
FORSCHUNG<br />
Biegeknicken von Stahlstützen im Brandfall<br />
Projektleitung: Prof. Dr. M. Fontana,<br />
Dr. M. Knobloch<br />
Mitarbeitende: J. Pauli, D. Somaini<br />
Projektpartner: Schweizerischer Nationalfonds,<br />
Bern<br />
Im Rahmen des Forschungsprojektes analysierten<br />
wir das Tragverhalten von Stahlstützen im Brand -<br />
fall unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Quer -<br />
schnitts tragfähigkeit sowie des Biegeknickens. Das<br />
Verhalten untersuchten wir mit Hilfe analytischer,<br />
experimenteller <strong>und</strong> numerischer Methoden.<br />
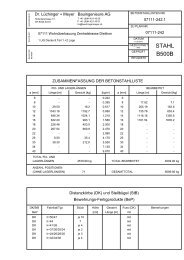
Die Beschreibung des Querschnitts- sowie des<br />
globalen Tragwiderstands unter Druck- sowie kombinierter<br />
Druck- <strong>und</strong> Biegebeanspruchung im<br />
Brand fall mit Hilfe experimentell abgesicherter Be -<br />
rech nungsmodelle stellte ein wesentliches Ziel un -<br />
se rer Forschungsarbeiten dar. Für den Querschnitts<br />
widerstand unter kombinierter Druck- <strong>und</strong><br />
zwei achsiger Biegebeanspruchung bei erhöhten<br />
Tem peraturen konnten auf der Gr<strong>und</strong>lage der Ver -<br />
suchs ergebnisse sowie einer umfangreichen nume -<br />
ri schen Parameterstudie Interaktionskurven abgeleitet<br />
werden. Die Beschreibung des Quer schnitts -<br />
wider stands im Brandfall stellt eine wesentliche<br />
Voraussetzung <strong>für</strong> die Darstellung des gr<strong>und</strong>legenden<br />
Tragverhaltens sowie der sicheren <strong>und</strong> wirtschaftlichen<br />
Dimensionierung <strong>und</strong> Bemessung von<br />
Stahlkonstruktionen dar. Eine Vergleichsstudie<br />
zeigte die teilweise sehr grossen Abweichungen der<br />
derzeit verwendeten vereinfachten Be rech nungs -<br />
mo delle <strong>für</strong> die Bemessung im Brandfall.<br />
Für die Beschreibung des Tragwiderstandes von<br />
Stahl stützen unter Druck- sowie kombinierter<br />
Druck- <strong>und</strong> einachsiger Biegebeanspruchung konnte<br />
ein analytisches Berechnungsmodell entwickelt<br />
wer den. Das Berechnungsmodell basiert auf um -<br />
fang reichen experimentellen <strong>und</strong> numerischen<br />
Unter suchungen. Diese Untersuchungen zeigten<br />
den entscheidenden Einfluss des thermischen<br />
Hoch temperaturkriechens sowohl auf das Stabilitätsverhalten<br />
sowie die Querschnittstragfähigkeit<br />
<strong>und</strong> führten zu einem Folgeprojekt zum Einfluss<br />
des thermischen Kriechens auf das Stabilitätsverhalten<br />
von Stahlkonstruktionen bei Brand.<br />
Buckling and flexural buckling of steel<br />
columns in fire<br />
The structural resistance of steel members, in particular<br />
columns or beam-columns, <strong>und</strong>er fire conditions<br />
is limited by three limit states and their interaction:<br />
First, full section yielding at elevated temperature<br />
(i.e. yield capacity) considering both, axial compression-bending<br />
moment interaction and non-uniform<br />
temperature distributions (limit state 1);<br />
second, local and/or distortional buckling (limit state<br />
2); and third, overall structural stability, especially<br />
flexural and lateral-torsional buckling (limit state 3).<br />
The reduction of steel strength during heating in<br />
fires as well as thermal gradients substantially affect<br />
the first limit state, while the reduced stiffness and<br />
the nonlinear stress-strain relationship of steel at elevated<br />
temperatures have a strong influence on local<br />
buckling and overall buckling behaviour. Analytical<br />
models used for fire design usually implicitly consider<br />
section yielding (limit state 1) and uniform temperature<br />
distributions. These models assume that<br />
members with no overall buckling effects, whose<br />
cross sections are classified as ‘plastic’ (Class 1),<br />
‘compact’ (Class 2) or ‘semi-compact’ (Class 3),<br />
reach their full plastic or elastic capacity, respectively,<br />
without developing local buckling deflections<br />
even <strong>und</strong>er fire conditions. However, elevated temperatures<br />
strongly influence the cross-sectional<br />
capacity and the local buckling behaviour of steel<br />
sections. Even cross-sections suitable for plastic<br />
design at ambient temperature may develop local<br />
buckling deflections in fires, caused by the large<br />
strains required to reach full section yielding due to<br />
the distinctly nonlinear stress-strain relationship for<br />
steel at elevated temperatures.<br />
In a comprehensive analytical, experimental and<br />
numerical study the cross-sectional capacity of steel<br />
sections in axial compression and bending as well<br />
as the overall structural behaviour of steel members<br />
at elevated temperatures <strong>und</strong>er fire conditions has<br />
been investigated. Normalized axial compressionbiaxial<br />
bending moment interaction graphs for the<br />
cross capacity as well as a generalized analytical<br />
model for the strength of slender columns in fires<br />
have been developed. The effects of the cross-sectional<br />
and overall slenderness ratio, steel grade,<br />
temperature, and production process (hot-rolled or<br />
welded) were addressed.<br />
51