- Page 1 and 2: October 2006 Volume 9 Number 4
- Page 3 and 4: Guidelines for authors Submissions
- Page 5 and 6: How Does Educational Technology Ben
- Page 7 and 8: Adaptivity is one of the most impor
- Page 9 and 10: 3. Ease of editing and updating: wh
- Page 11 and 12: Accessible and personalized Learnin
- Page 13 and 14: From this definition, we figured ou
- Page 15 and 16: Verifying contents Figure 3. The pa
- Page 17 and 18: Figure 7. The ISA on line interface
- Page 19 and 20: Adaptive Technology Resource Centre
- Page 21 and 22: World Wide Web Consortium (1999a).
- Page 23 and 24: guiding and supporting environment
- Page 25 and 26: As an example, to improve the acces
- Page 27 and 28: option). Although this finding migh
- Page 29 and 30: of eLearning content and enhance th
- Page 31 and 32: Hodgings, W. & Duval, E. (2002). IE
- Page 33 and 34: the entire course of study. This sy
- Page 35: information useful for the contextu
- Page 39 and 40: Vincenzo, a second year student, ne
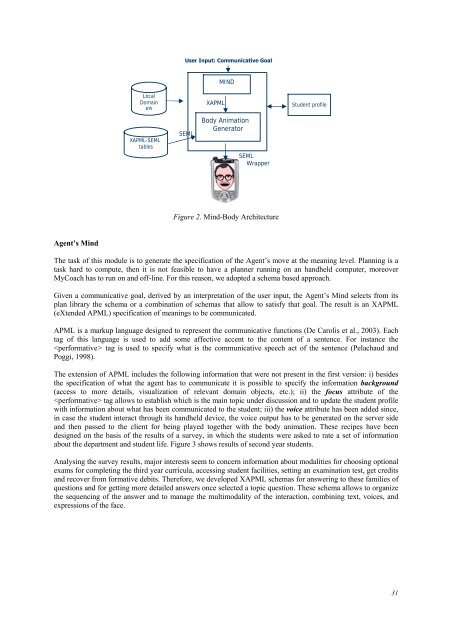
- Page 41 and 42: Evaluation Recently embodied conver
- Page 43 and 44: The interaction may be performed on
- Page 45 and 46: Poggi, I., Pelachaud, C., & de Rosi
- Page 47 and 48: Lanzilotti, R., Ardito, C., & Costa
- Page 49 and 50: quality in use, which is measured b
- Page 51 and 52: process of designing high quality c
- Page 53 and 54: eLSE methodology Designers and eval
- Page 55 and 56: Execution phase Execution phase act
- Page 57 and 58: on the inspection process and, cons
- Page 59 and 60: Piccinini, N., & Scollo, G. (2006).
- Page 61 and 62: Answers and reinforcement A.1: Use
- Page 63 and 64: potential project ideas (from pure
- Page 65 and 66: For each column in Table 2, the sum
- Page 67 and 68: educational goals and the various r
- Page 69 and 70: A new computerized Records Manageme
- Page 71 and 72: eflected in artifacts and other str
- Page 73 and 74: any distributed community include b
- Page 75 and 76: message in order to obtain a respon
- Page 77 and 78: Figure 3. Social network after intr
- Page 79 and 80: increased face-to-face collaboratio
- Page 81 and 82: References Bogenrieder, I. (2002).
- Page 83 and 84: Donoghue, S. L. (2006). Institution
- Page 85 and 86: contemplate part-time, rather than
- Page 87 and 88:
espective institutions. The primary
- Page 89 and 90:
greater flexibility in course selec
- Page 91 and 92:
Cost-benefit One distinct benefit o
- Page 93 and 94:
Resources The development of online
- Page 95 and 96:
courses where it is has little pote
- Page 97 and 98:
A fellowship programme, such as the
- Page 99 and 100:
Moore, M.G. (1998). Introduction. I
- Page 101 and 102:
Software reuse has two dimensions,
- Page 103 and 104:
Courseware development process mode
- Page 105 and 106:
Didactics analysis This phase consi
- Page 107 and 108:
Process didactics design We focus o
- Page 109 and 110:
The repository is organized into co
- Page 111 and 112:
the analysis and the design phase o
- Page 113 and 114:
Figure 12. Weaving content and dida
- Page 115 and 116:
complete user-specific (author, ins
- Page 117 and 118:
References ADL (Advanced Distribute
- Page 119 and 120:
Bender, D. M., & Vredevoogd, J. D.
- Page 121 and 122:
(see Figure 2). The incorporation o
- Page 123 and 124:
Figure 4: Example of Summary Image
- Page 125 and 126:
The competitive nature of design cl
- Page 127 and 128:
Dias, L. B. (1999, November). Integ
- Page 129 and 130:
materials built into the system. Th
- Page 131 and 132:
This theory of multimedia learning
- Page 133 and 134:
E-Tutor (with video). Two weeks aft
- Page 135 and 136:
empirically tested in TML environme
- Page 137 and 138:
Rieber, L. P., (1990). Animation in
- Page 139 and 140:
Appendix B The following 44 items r
- Page 141 and 142:
Appendix C A Sample of Exam Questio
- Page 143 and 144:
Appendix D Perceived Usefulness Que
- Page 145 and 146:
Kirkpatrick, and Peck (2001) have a
- Page 147 and 148:
2001). The system thus aims to assi
- Page 149 and 150:
a strong agreement between the two
- Page 151 and 152:
of the dynasty. 3. Information on
- Page 153 and 154:
Comparing works designed using the
- Page 155 and 156:
Tselios, N., Stoica, A., Maragoudak
- Page 157 and 158:
strategies during their interaction
- Page 159 and 160:
P(B|D) is the probability of a netw
- Page 161 and 162:
Online help adaptation using Bayesi
- Page 163 and 164:
AUSM that will return the most prob
- Page 165 and 166:
direct experimentation with a new s
- Page 167 and 168:
Figure 7. An example of use of the
- Page 169 and 170:
Cooper, J. & Herskovits, E. (1992).
- Page 171 and 172:
Goldberg, A. K., & Riemer, F. J. (2
- Page 173 and 174:
In addition to convenience, propone
- Page 175 and 176:
members increased flexibility. They
- Page 177 and 178:
Oppenheimer, T. (1997, July). The c
- Page 179 and 180:
The basis of reform in science educ
- Page 181 and 182:
technology and are not confident in
- Page 183 and 184:
participants that learning as a gro
- Page 185 and 186:
A hierarchy of Systems Identifying
- Page 187 and 188:
the change agents to recognize the
- Page 189 and 190:
Nonis, A. S., & O’Bannon, B. (200
- Page 191 and 192:
maintaining the interest levels of
- Page 193 and 194:
Focus group interviews with our stu
- Page 195 and 196:
course and again at the end of the
- Page 197 and 198:
second phase of valuing, commitment
- Page 199 and 200:
Kinzie, M. B., Whitaker, S. D., Nee
- Page 201 and 202:
Although this work is based on a st
- Page 203 and 204:
Website Design The MTP website (www
- Page 205 and 206:
Researchers, for review and coding
- Page 207 and 208:
quality that are the focus of the M
- Page 209 and 210:
Kelley, M. A., Whitaker, S. D., Nee
- Page 211 and 212:
or underserved populations. For exa
- Page 213 and 214:
2004 Baruch College Computer Center
- Page 215 and 216:
professional-level tools and resour
- Page 217 and 218:
Third, with the exception of the Om
- Page 219 and 220:
Hepp, P., Hinostroza, E., Laval, E.
- Page 221 and 222:
The AccessForAll strategy complemen
- Page 223 and 224:
of people with special needs, or di
- Page 225 and 226:
(including where their search for r
- Page 227 and 228:
international standard. The ISO pro
- Page 229 and 230:
information will be expressed using
- Page 231 and 232:
DC Metadata Terms: http://dublincor
- Page 233 and 234:
Choquet, C., & Corbière, A. (2006)
- Page 235 and 236:
TEL Standards, Specifications and P
- Page 237 and 238:
The Resources Management Process ma
- Page 239 and 240:
Step 1: Instantiation of the enterp
- Page 241 and 242:
Step 5: Instantiation of the techno
- Page 243 and 244:
correlation of the different viewpo
- Page 245 and 246:
Hummel, H., Manderveld, J., Tatters
- Page 247 and 248:
Karagiannidis, C. (2006). Book revi
- Page 249 and 250:
Glenn, L. (2006). Book review: Visu