You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
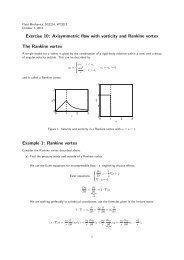
Stability and sensitivity analysis of separation bubbles.<br />
L.Marino ∗ , P.Luchini †<br />
In the present contribution the linear stability of an incompressible flow in the<br />
presence of a recirculating bubble is considered.<br />
The problem is relevant to aeronautical applications; in fact separation bubbles<br />
can arise near the leading edge of airfoils, under particular flight conditions, and can<br />
dramatically change their performance (lift and drag).<br />
The stability properties of separation bubbles on flat plates have been studied by<br />
past authors through an approach based on parallel and weakly non-parallel approximations<br />
1 , or by direct numerical simulation 2 . In both cases the separation bubble<br />
has been induced by giving a predefined adverse pressure gradients to boundary-layer<br />
velocity profiles.<br />
Here the analysis is carried out both in a flat geometry with a prescribed external<br />
pressure gradient and in the case of flow over a curved surface.<br />
The properties of the ensuing global instability are obtained without any parallelflow<br />
approximation; we remind that the term ”global” is here referred to instabilities<br />
not amenable to the quasi-parallel approximation 3 . Consequently, the problem is<br />
studied by solving the complete Navier-Stokes equations.<br />
The critical Reynolds number and the structure of the possible instability of the<br />
flow are the main topics of the present investigation. Moreover the sensitivity characteristics<br />
are determined, by an adjoint analysis of the relevant eigenvalue problem.<br />
In particular the effects of inflow disturbances and of structural perturbations (which<br />
comprise base flow and boundary conditions changes) are analysed and discussed.<br />
A general three-dimensional perturbation is assumed, with a sinusoidal dependence<br />
on the spanwise coordinate. Such a formulation leads to a large-scale eigenvalue<br />
problem which is then solved by an inverse-iteration algorithm.<br />
A particular attention was given to the boundary conditions necessary in order<br />
to achieve an asymptotic behaviour of both base flow and perturbation at the upper<br />
computational boundary. The influence of different choices of such conditions will<br />
also be discussed.<br />
∗Dipartimento di Meccanica e Aeronautica, Universitá degli studi di Roma “La Sapienza”, Via<br />
Eudossiana 18, Roma, I-00184.<br />
† Dipartimento di Ingegneria Meccanica, Universitá di Salerno, Fisciano (SA), I-84084.<br />
1D.A. Hammond, L.G. Redenkopp, Local and global properties of separation bubbles, Eur. J.<br />
Mech. B/Fluids, 17,1998.<br />
2U. Rist, U. Maucher, Investigations of time-growing instabilities in laminar separation bubbles,<br />
Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids, 21,2002.<br />
3J. -M. Chomaz, Global instabilities in spatially developing flows: Non-normality and nonlinearity,<br />
Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech., 37,2005.<br />
83