You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
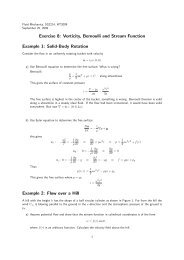
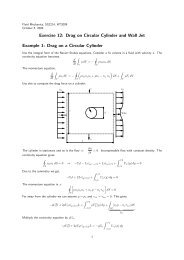
Computations of turbulent boundary layers with<br />
streamwise and spanwise pressure gradients<br />
A. Jammalamadaka a, H. Nagib a and K. Chauhan a<br />
The performance of four popular turbulence models, namely, Spalart-Allmaras, k-,<br />
SST and RSM, is evaluated for prediction of turbulent boundary layers subjected to<br />
streamwise and spanwise pressure gradients. The computations are made at one to<br />
one scale for a recently completed 2-D turbulent boundary layer experiment1,2 and a<br />
previously measured 3-D turbulent boundary layer3. Both experiments were carefully<br />
documented with the aid of independent measurement of skin friction. The 2-D<br />
boundary layer comparisons are made for adverse (APG) and favorable pressure<br />
gradients with Re in the range 10,000 to 50,000. The two-equation models fared<br />
better than the one-equation model when the mean velocity and skin friction<br />
coefficient are compared. Overall, the models fail to replicate the non-universal<br />
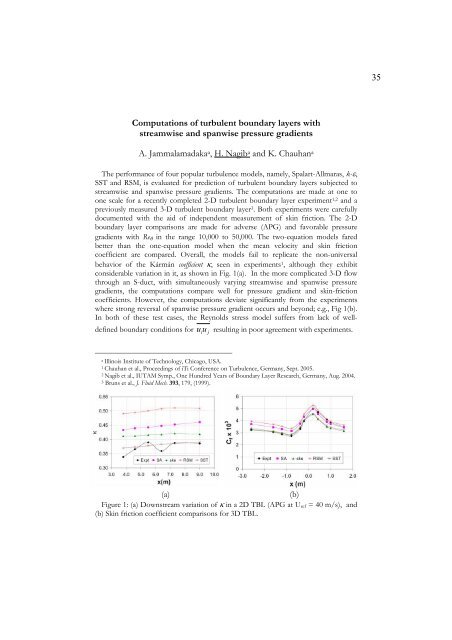
behavior of the Kármán coefficient , seen in experiments1, although they exhibit<br />
considerable variation in it, as shown in Fig. 1(a). In the more complicated 3-D flow<br />
through an S-duct, with simultaneously varying streamwise and spanwise pressure<br />
gradients, the computations compare well for pressure gradient and skin-friction<br />
coefficients. However, the computations deviate significantly from the experiments<br />
where strong reversal of spanwise pressure gradient occurs and beyond; e.g., Fig 1(b).<br />
In both of these test cases, the Reynolds stress model suffers from lack of welldefined<br />
boundary conditions for u iu j resulting in poor agreement with experiments.<br />
___________________________________<br />
a Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, USA.<br />
1 Chauhan et al., Proceedings of iTi Conference on Turbulence, Germany, Sept. 2005.<br />
2 Nagib et al., IUTAM Symp., One Hundred Years of Boundary Layer Research, Germany, Aug. 2004.<br />
3 Bruns et al., J. Fluid Mech. 393, 179, (1999).<br />
(a) (b)<br />
Figure 1: (a) Downstream variation of in a 2D TBL (APG at Uref = 40 m/s), and<br />
(b) Skin friction coefficient comparisons for 3D TBL.<br />
35