View - DSpace UniPR
View - DSpace UniPR
View - DSpace UniPR
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PNAs: from birth to adulthood<br />
between the 2’oxygen and the 4’ carbon of the ribose ring 6 . Pure LNA oligonucleotides can<br />
be used, as well as mixed oligonucleotides with standard DNA monomers and LNA<br />
monomers, obtaining an increased affinity for DNA and RNA, and resistance to enzymes. The<br />
good cellular uptake also allowed applications in gene therapy with good results 7 . In<br />
morpholino oligonucleotides (MF), the ribose ring is replaced by a morpholino moiety and<br />
phosphoroamidate linkages are used instead of phosphodiester bonds 8 . The affinity for<br />
complementary sequences is similar to that of DNA oligonucleotides, the enzymatic stability<br />
is high and unspecific interactions with proteins are not observed, allowing for their use for<br />
in-vivo applications. Cyclohexene nucleic acids (CeNA) 9 , tricyclo-DNA (tcDNA) 10 , 2’-<br />
deoxy-2’-fluoro-β-D-arabino nucleic acid (FANA) 11 are other types of DNA analogues which<br />
show an increased affinity towards DNA and RNA, if compared to standard oligonucleotides.<br />
The affinity usually increases because of the absence of negative charges in the backbone,<br />
avoiding electrostatic repulsions with the target DNA strand, or for the introduction of more<br />
rigid groups, able to maintain the correct nucleobase orientation to form Watson-Crick<br />
interactions. The increase of in vivo stability usually observed is due to the inability of<br />
degrading enzymes to recognize the modified structures 12 .<br />
1.3 PNA<br />
The quest for the development of a high performance DNA analogue led in 1991 to the<br />
synthesis of another type of modified nucleic acids, called Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs) 13 .<br />
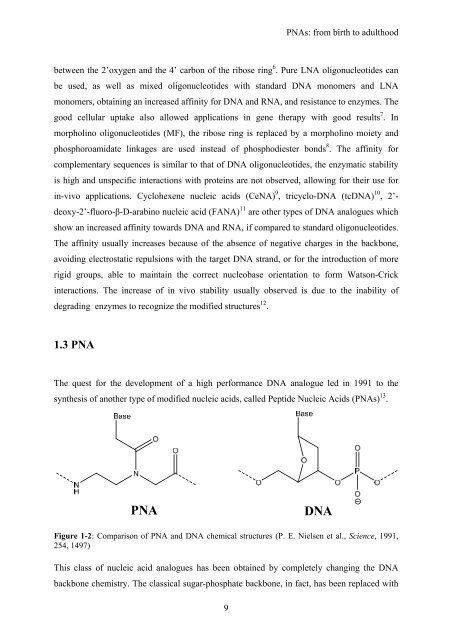
PNA<br />
DNA<br />
Figure 1-2: Comparison of PNA and DNA chemical structures (P. E. Nielsen et al., Science, 1991,<br />
254, 1497)<br />
This class of nucleic acid analogues has been obtained by completely changing the DNA<br />
backbone chemistry. The classical sugar-phosphate backbone, in fact, has been replaced with<br />
9