View - DSpace UniPR
View - DSpace UniPR
View - DSpace UniPR
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PNAs: from birth to adulthood<br />
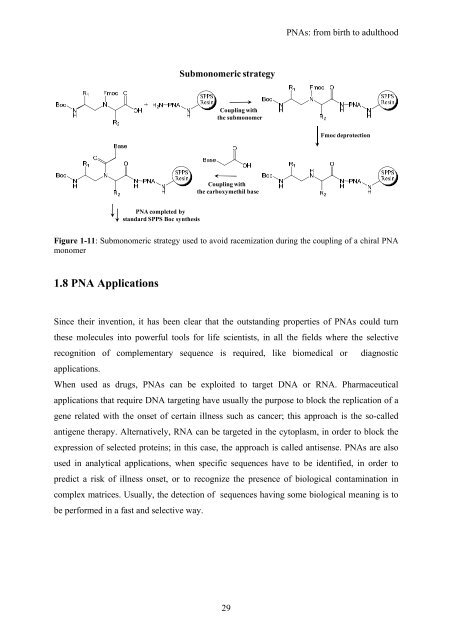
Submonomeric strategy<br />
Coupling with<br />
the submonomer<br />
Fmoc deprotection<br />
Coupling with<br />
the carboxymethil base<br />
PNA completed by<br />
standard SPPS Boc synthesis<br />
Figure 1-11: Submonomeric strategy used to avoid racemization during the coupling of a chiral PNA<br />
monomer<br />
1.8 PNA Applications<br />
Since their invention, it has been clear that the outstanding properties of PNAs could turn<br />
these molecules into powerful tools for life scientists, in all the fields where the selective<br />
recognition of complementary sequence is required, like biomedical or diagnostic<br />
applications.<br />
When used as drugs, PNAs can be exploited to target DNA or RNA. Pharmaceutical<br />
applications that require DNA targeting have usually the purpose to block the replication of a<br />
gene related with the onset of certain illness such as cancer; this approach is the so-called<br />
antigene therapy. Alternatively, RNA can be targeted in the cytoplasm, in order to block the<br />
expression of selected proteins; in this case, the approach is called antisense. PNAs are also<br />
used in analytical applications, when specific sequences have to be identified, in order to<br />
predict a risk of illness onset, or to recognize the presence of biological contamination in<br />
complex matrices. Usually, the detection of sequences having some biological meaning is to<br />
be performed in a fast and selective way.<br />
29