Alma Mater Studiorum Universit`a degli Studi di Bologna ... - Inaf
Alma Mater Studiorum Universit`a degli Studi di Bologna ... - Inaf
Alma Mater Studiorum Universit`a degli Studi di Bologna ... - Inaf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
20 2. The X-ray environment of ra<strong>di</strong>o galaxies<br />
-17 00 00<br />
2 4 6 8<br />
-17 00 00<br />
30<br />
30<br />
DECLINATION (J2000)<br />
01 00<br />
30<br />
02 00<br />
DECLINATION (J2000)<br />
01 00<br />
30<br />
02 00<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
Outer<br />
30<br />
30<br />
03 00<br />
22 14 32 30 28 26 24 22 20<br />
RIGHT ASCENSION (J2000)<br />
03 00<br />
22 14 32 30 28 26 24 22 20 18<br />
RIGHT ASCENSION (J2000)<br />
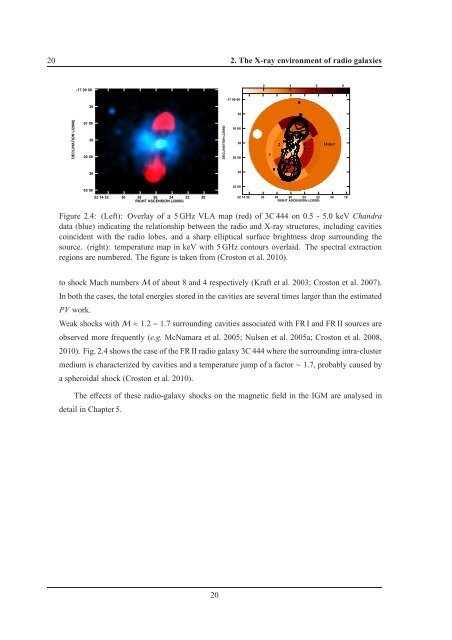
Figure 2.4: (Left): Overlay of a 5 GHz VLA map (red) of 3C 444 on 0.5 - 5.0 keV Chandra<br />
data (blue) in<strong>di</strong>cating the relationship between the ra<strong>di</strong>o and X-ray structures, inclu<strong>di</strong>ng cavities<br />
coincident with the ra<strong>di</strong>o lobes, and a sharp elliptical surface brightness drop surroun<strong>di</strong>ng the<br />
source. (right): temperature map in keV with 5 GHz contours overlaid. The spectral extraction<br />
regions are numbered. The figure is taken from (Croston et al. 2010).<br />
to shock Mach numbersMof about 8 and 4 respectively (Kraft et al. 2003; Croston et al. 2007).<br />
In both the cases, the total energies stored in the cavities are several times larger than the estimated<br />
PV work.<br />
Weak shocks withM≈1.2−1.7 surroun<strong>di</strong>ng cavities associated with FR I and FR II sources are<br />
observed more frequently (e.g. McNamara et al. 2005; Nulsen et al. 2005a; Croston et al. 2008,<br />
2010). Fig. 2.4 shows the case of the FR II ra<strong>di</strong>o galaxy 3C 444 where the surroun<strong>di</strong>ng intra-cluster<br />
me<strong>di</strong>um is characterized by cavities and a temperature jump of a factor∼1.7, probably caused by<br />
a spheroidal shock (Croston et al. 2010).<br />
The effects of these ra<strong>di</strong>o-galaxy shocks on the magnetic field in the IGM are analysed in<br />
detail in Chapter 5.<br />
20