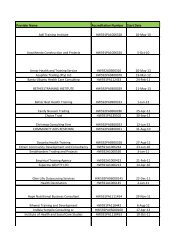
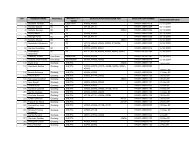
sector skills plan for the health sector in south africa
sector skills plan for the health sector in south africa
sector skills plan for the health sector in south africa
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Recent research has projected an <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> demand <strong>for</strong> service and a concomitant <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> human<br />
resources required to meet <strong>the</strong> demand. The scheme will extend access to private care free of charge<br />
and will <strong>in</strong>crease demand <strong>for</strong> services of GPs and specialists. 132 More patients will be attracted to<br />
medical practitioners and hospitals <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> private <strong>sector</strong> and away from public cl<strong>in</strong>ics and public<br />
hospitals. 133<br />
It has been mooted that norms and standards <strong>for</strong> care will be set to enhance quality of service and care<br />
<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> public <strong>sector</strong>. Fur<strong>the</strong>r, packages of care conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g standard lists of services to be delivered at<br />
each level of care will be designed. Implementation of <strong>the</strong>se policies may have an impact on <strong>the</strong> present<br />
<strong>skills</strong> base, <strong>in</strong> that <strong>the</strong>re may be gaps or shortages of <strong>skills</strong> to meet <strong>the</strong> standards to be <strong>in</strong>troduced.<br />
Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and <strong>skills</strong> development <strong>in</strong>terventions will be required to deal with such <strong>skills</strong> gaps and<br />
shortages.<br />
In <strong>the</strong> NHI system itself, considerable managerial, f<strong>in</strong>ancial and <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation technology management<br />
<strong>skills</strong> will be required to monitor usage and benefits offered, <strong>the</strong> distribution of resources, and <strong>the</strong> costs<br />
of <strong>the</strong> scheme. 134<br />
3.10.4 HIV AND AIDS POLICIES<br />
By 2010 <strong>the</strong> number of hospital or cl<strong>in</strong>ic visits associated with HIV and AIDS approached 30 million per<br />
annum. 135 An estimated 740 000 patients were on anti-retroviral treatment (ART) by 2009.<br />
In April 2010 government announced <strong>the</strong> accelerated implementation of HIV test<strong>in</strong>g and ART<br />
programmes to <strong>in</strong>clude more people on treatment. President Zuma announced that 15 million South<br />
Africans will be HIV tested by June 2011 and be granted access to AIDS medication if <strong>the</strong>y require it.<br />
Estimates are that 2 million people may require ART with<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> next few years. 136 Clearly, additional<br />
human resources will be required if <strong>the</strong> ART population is to <strong>in</strong>crease almost three-fold. Health<br />
economists predict that more than 25% of current public <strong>health</strong> resources will be required <strong>for</strong> ART over<br />
<strong>the</strong> next 10 years, and by 2020 <strong>the</strong> resource needs will be 40% of resources currently available. 137<br />
It is reported that <strong>the</strong> DoH <strong>plan</strong>s to equip more than 4300 sites to adm<strong>in</strong>ister <strong>the</strong> treatment (or almost<br />
four times <strong>the</strong> number of police stations <strong>in</strong> South Africa) and to tra<strong>in</strong> 4800 nurses and lay counsellors to<br />
<strong>in</strong>itiate and manage <strong>the</strong> AIDS treatment. 138 The scale of <strong>the</strong> programme will require <strong>the</strong> appo<strong>in</strong>tment of<br />
more adm<strong>in</strong>istrative support staff (to order, collect and distribute drugs) and more skilled <strong>health</strong><br />
managers to implement and oversee operations.<br />
132 Van der Berg, S., Burger, R., Theron, N. et al. 2010. Econex. F<strong>in</strong>ancial Implications of a National Health Insurance Plan <strong>for</strong><br />
South Africa.<br />
133 Van der Berg, S., Burger, R., Theron, N. et al. 2010. Econex. F<strong>in</strong>ancial Implications of a National Health Insurance Plan <strong>for</strong><br />
South Africa.<br />
134 Macheke, C. 2010. HWSETA Health Sector Basel<strong>in</strong>e Study.<br />
135 National Treasury. Budget Review 2010.<br />
136 Ste<strong>in</strong>berg, J. “The state wants our blood, to stop <strong>the</strong> three-letter plague”. Sunday Times 2 May 2010, p. 9.<br />
137 HEU In<strong>for</strong>mation Sheet 1. 2009. “Public <strong>sector</strong> <strong>health</strong> care spend<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> South Africa”. Health Economics Unit, University of<br />
Cape Town. Published at http://www.heu-uct.org.za (Accessed August 2010).<br />
138 Ste<strong>in</strong>berg, J. “The state wants our blood, to stop <strong>the</strong> three-letter plague”. Sunday Times 2 May 2010, p. 9.<br />
38